Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Inverter vs UPS
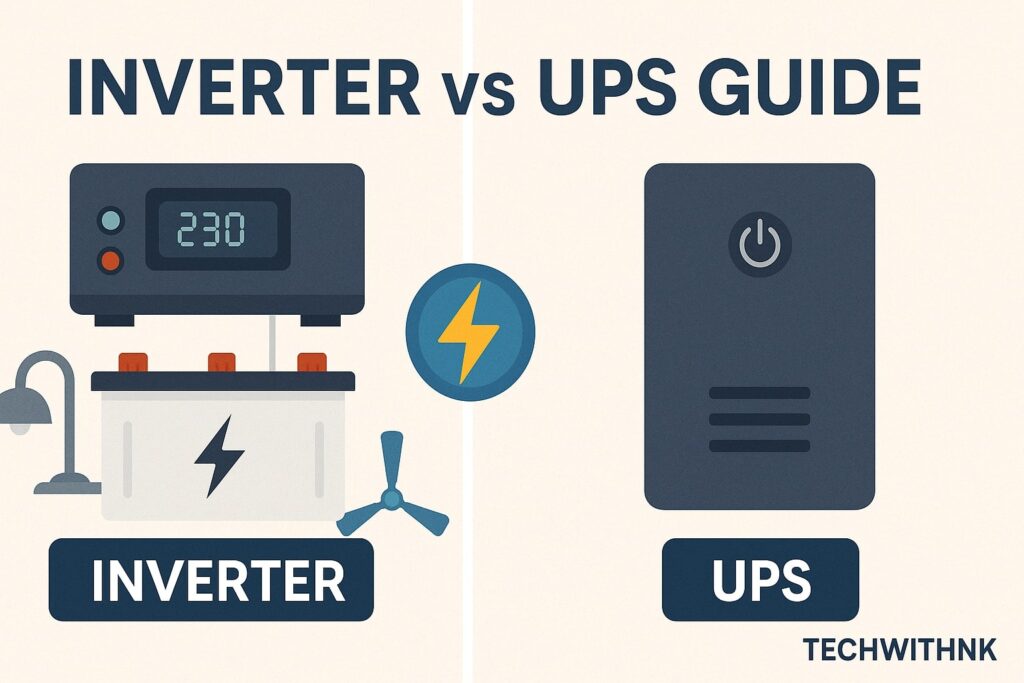
Power cuts and voltage fluctuations are still a reality in many parts of India. Whether you are working from home, running a small business, or simply want uninterrupted electricity for your household, choosing between an inverter and a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) can be confusing. Both systems aim to provide backup power, but they serve slightly different purposes.
This guide explains everything you need to know about inverters and UPS systems, their types, advantages, and how to select the right one based on your needs.

What is an Inverter?
An inverter is a device that converts DC (Direct Current) stored in a battery into AC (Alternating Current) used by household appliances. It provides backup power during long power cuts.
Key Features of Inverters:
Works with large batteries (100Ah–220Ah and above).
Provides power backup for hours.
Suitable for running appliances like fans, lights, TV, computers, and sometimes refrigerators.
Takes a few seconds to switch on during a power cut.
What is a UPS?
A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) is a device designed to provide instant backup power to sensitive equipment like computers, Wi-Fi routers, and servers. Unlike inverters, a UPS has zero switching time—ensuring that your devices never shut down during an outage.
Key Features of UPS:
Immediate power backup (no delay).
Smaller battery compared to inverters.
Ideal for computers, routers, CCTV systems, and servers.
Backup time is usually limited to 15–60 minutes.

Inverter vs UPS: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Inverter | UPS |
|---|---|---|
| Backup Time | Hours (2–10 hours) | Minutes (15–60 minutes) |
| Switching Time | 2–5 seconds | 0 seconds (instant) |
| Appliances | Fans, lights, TV, fridge | Computers, routers, servers |
| Battery Size | Large (100Ah–220Ah+) | Small (7Ah–20Ah) |
| Cost | Higher (depends on battery) | Lower (desktop UPS affordable) |
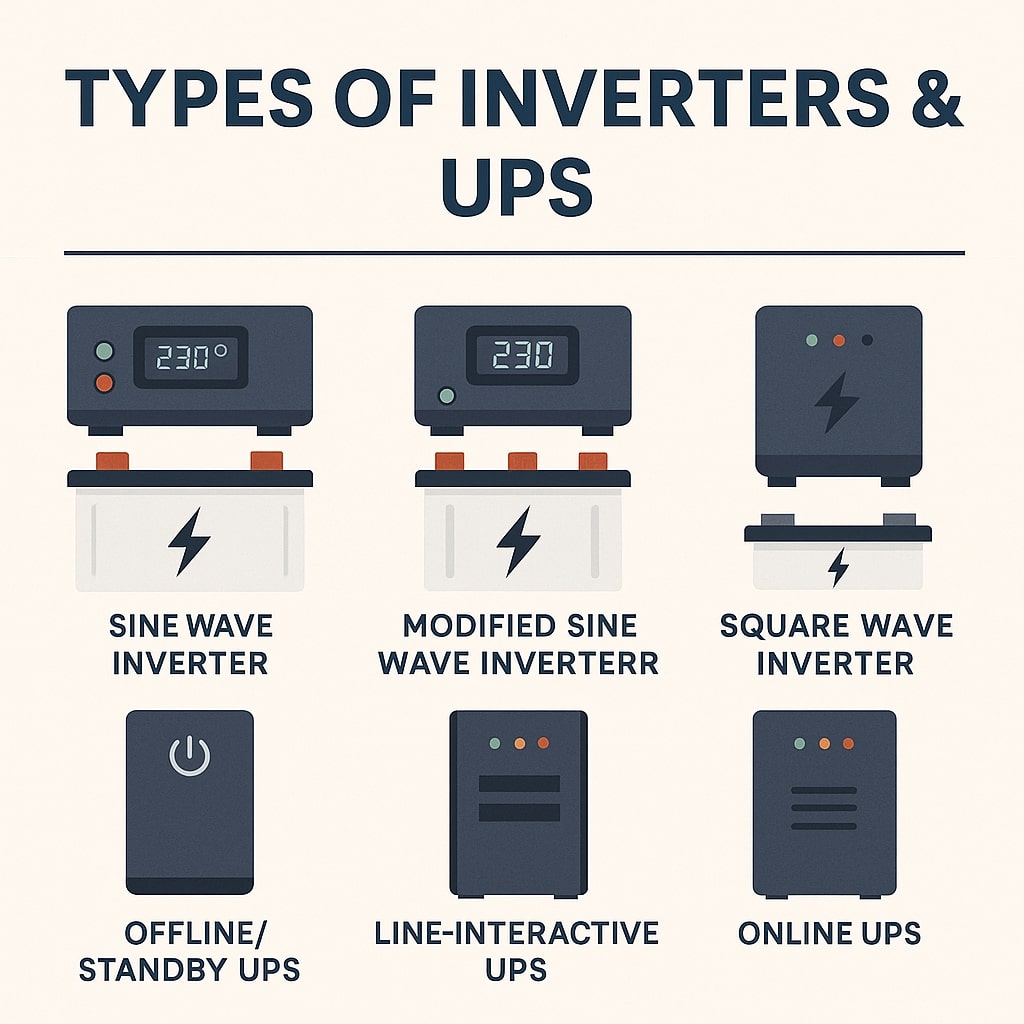
Types of Inverters
Sine Wave Inverter – Produces smooth AC power; safe for sensitive appliances like laptops, TVs, and refrigerators.
Modified Sine Wave Inverter – Cheaper but may not support all appliances smoothly.
Square Wave Inverter – Least expensive; suitable only for basic devices like bulbs and fans.
Types of UPS Systems
Offline/Standby UPS – Basic and affordable; switches to battery when power goes out.
Line-Interactive UPS – Provides automatic voltage regulation; good for home offices.
Online UPS – Continuous power supply with no interruptions; used in data centers and hospitals.
How to Choose Between Inverter vs UPS
Purpose:
For computers, routers, and sensitive devices → Choose UPS.
For long power cuts and multiple appliances → Choose Inverter.
Power Requirement:
Small load (single PC, Wi-Fi router) → UPS.
Heavy load (fans, TV, fridge, lights) → Inverter with large battery.
Backup Time Needed:
Few minutes → UPS.
Several hours → Inverter.
Budget:
UPS: ₹2,000–₹10,000 (depending on capacity).
Inverter: ₹10,000–₹40,000 (with battery).
- visit on Amazon

Best Practices for Using Inverter & UPS
Always buy from trusted brands like Luminous, Microtek, APC, V-Guard, or Zebronics.
Ensure proper battery maintenance (check water levels in tubular batteries).
Use correct wiring and grounding for safety.
Place inverter/UPS in a ventilated area.
Avoid overloading the system.
Common Mistakes People Make
Buying an inverter without calculating power needs.
Using modified sine wave inverters for sensitive devices (causes damage).
Expecting UPS to run household appliances for hours.
Ignoring regular battery maintenance.
Conclusion
Both inverter and UPS systems play an important role in ensuring uninterrupted power. If you want long backup for household appliances, an inverter is the best choice. If your priority is to keep computers and routers safe from sudden shutdowns, a UPS is essential.
By understanding your power requirements, budget, and backup needs, you can confidently choose the right system for your home or office.
Can I use both inverter and UPS at home?
Yes. Many households use an inverter for appliances and a UPS for computers or Wi-Fi routers.
Which is better: inverter or UPS?
Neither is “better”—it depends on the usage. UPS is best for sensitive electronics, while inverters are better for longer power cuts.
How long do inverter batteries last?
Typically, 3–5 years with proper maintenance.