Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
When you think of the internet, one name almost instantly comes to mind: Google. What began as a research project at Stanford University has evolved into the most powerful technology company in the world, shaping how billions of people access information, communicate, navigate, shop, and even think.
Google is more than just a search engine. It is a tech ecosystem that powers smartphones (Android), dominates online advertising (Google Ads), provides business tools (Google Workspace), leads in video content (YouTube), drives navigation (Google Maps), innovates in cloud computing (Google Cloud), and pushes boundaries in artificial intelligence (Google DeepMind, Gemini AI).
This blog explores Google’s journey, ecosystem, revenue model, controversies, and future directions.
History of Google
Founding Story
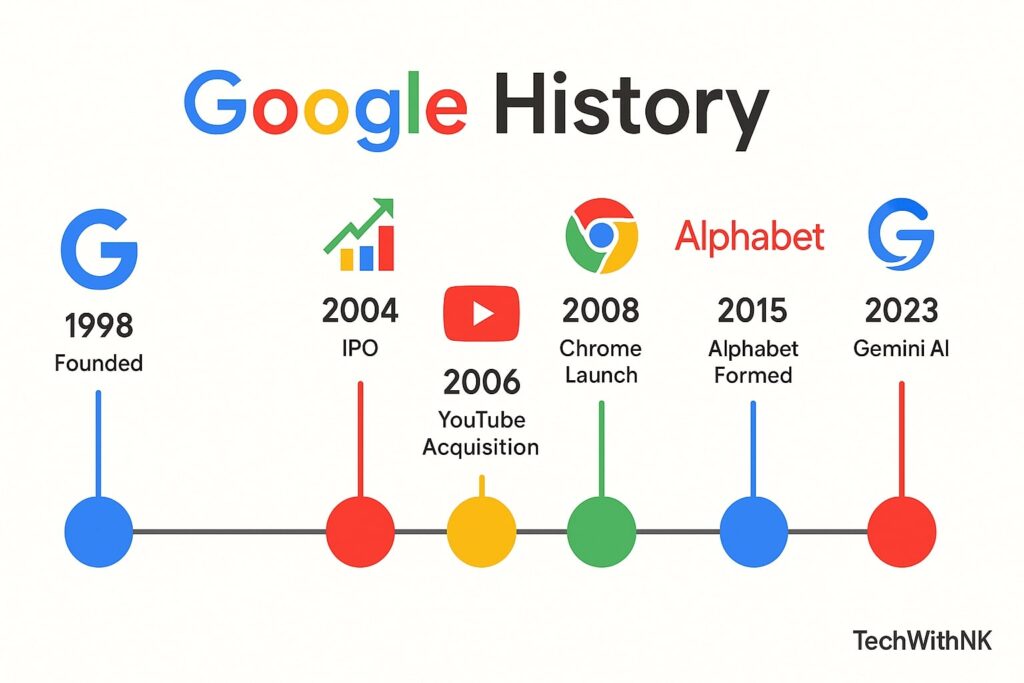
Google started in 1996 as a research project by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, Ph.D. students at Stanford University. The idea was to create a search engine that ranked web pages based on backlinks — called BackRub.
In 1998, Google was officially founded. The name comes from the mathematical term “googol” (1 followed by 100 zeros), symbolizing the mission to organize the vast information of the internet.
Early Growth
1999: Google received $25 million in venture capital.
2000: Became the largest search engine, partnering with Yahoo.
2001: Eric Schmidt joined as CEO.
2004: Google went public (IPO), raising $1.67 billion.
Becoming Alphabet Inc.
In 2015, Google restructured under Alphabet Inc., making Google its largest subsidiary. This allowed diversification into other fields (healthcare, self-driving cars, smart devices, etc.).
Google’s Ecosystem & Products
Google is no longer just a search engine — it’s a universe of products that billions of people rely on daily.
Google Search
The world’s #1 search engine with over 90% market share.
Handles over 8.5 billion searches per day.
Uses advanced algorithms, machine learning, and AI (like RankBrain, BERT, MUM) to deliver results.
Google Ads & Marketing
Google earns most revenue through advertising.
Google Ads allows businesses to show ads in search results, YouTube, and partner sites.
Google AdSense lets website owners earn money by displaying ads.
Gmail
Launched in 2004 with 1GB storage, Gmail revolutionized email.
Now, it has over 1.5 billion users.
Features: Smart Compose, AI spam filters, integration with Workspace.
YouTube
Acquired in 2006 for $1.65 billion.
Now the second most visited website in the world.
Over 2.7 billion monthly users.
Main revenue source: Ads, YouTube Premium, Super Chat, Memberships.
Google Maps & Navigation
Launched in 2005, used by billions for directions, traffic updates, and businesses.
Powers ride-sharing apps, food delivery, logistics.
Integration with AR (Live View).
Android & Mobile Ecosystem
Acquired in 2005, Android is now the world’s most used mobile OS (70% market share).
Google Play Store connects apps, games, and media.
Powers Pixel phones, wearables, smart TVs, and more.
Google Chrome & Web Tools
Chrome browser launched in 2008, now the #1 browser worldwide.
Tools: Google Docs, Sheets, Drive, Calendar → part of Google Workspace.
Free & collaborative tools dominate education and business.
Google Cloud
Competes with AWS & Microsoft Azure.
Provides cloud storage, AI/ML services, enterprise solutions.
Major clients: Spotify, Twitter, PayPal.
Google AI & DeepMind
Google AI develops natural language, image recognition, and robotics.
DeepMind (acquired 2014) achieved breakthroughs like AlphaGo, protein folding predictions.
Gemini AI is Google’s answer to OpenAI’s ChatGPT.
Hardware (Pixel, Nest, Fitbit)
Pixel smartphones, Chromebooks, Nest smart home devices, Fitbit wearables.
Competing with Apple’s hardware ecosystem.
Google’s Business Model
Google’s main revenue comes from advertising.
Ads (80% of revenue): Search ads, YouTube ads, AdSense.
Cloud (10–15%): Enterprise solutions, AI services.
Hardware & Other (5–10%): Pixel, Nest, Fitbit, Google Play.
2024 Revenue: $307 billion (Alphabet’s annual report).
Impact of Google
On the Internet
Made information universally accessible.
Standardized online advertising.
Created tools like Gmail, Docs, Maps.
On Businesses
Small businesses can reach global markets via Google Ads & Maps.
YouTube created the creator economy.
On Society
Google has changed how people learn, shop, travel, and communicate.
Enabled free education through YouTube, Google Scholar, Google Books.
Criticisms & Controversies
Privacy concerns: Tracking user data across apps.
Monopoly accusations: Multiple antitrust lawsuits (USA, EU, India).
Censorship issues: Content moderation on YouTube & Search.
Employee protests: Over military contracts, workplace culture.
Competition: Apple (iOS, Safari), Microsoft (Bing, Azure, AI), Amazon (AWS), OpenAI (ChatGPT).
Future of Google
Google’s future lies in AI, cloud, and new technologies:
Gemini AI → integrating generative AI into Search, Workspace, and YouTube.
Quantum Computing → Google’s Sycamore quantum computer.
Augmented Reality & XR → Smart glasses, AR navigation.
Green Tech → 100% carbon-free energy by 2030.
Conclusion
Google has transformed from a search startup to the world’s most influential tech company. Its impact on communication, learning, business, and entertainment is unmatched. However, with growing power comes responsibility — especially regarding privacy, monopolistic practices, and ethical AI.
The future of Google lies in AI, quantum computing, AR/VR, and green technology. Whether admired or criticized, one thing is clear: Google is the backbone of the modern internet age.
Who founded Google?
Larry Page and Sergey Brin founded Google in 1998 at Stanford University.
hy is Google called Google?
It comes from the word googol, meaning 10¹⁰⁰, symbolizing huge information.
What is Google’s parent company?
Alphabet Inc. (formed in 2015).














