Table of Contents
Toggle☀️ Introduction: Why Go Solar in 2025
As electricity prices rise and environmental awareness grows, solar energy has become one of the most reliable and affordable renewable energy options for homeowners.
In India, the government’s Rooftop Solar Programme and MNRE subsidies make solar panel installation more cost-effective than ever.
But before you buy, you must answer a key question:
👉 Should you choose an On-Grid, Off-Grid, or Hybrid solar system?
This detailed Solar Panel Buying Guide by TechWithNK will help you understand:
How solar panels work,
The difference between on-grid and off-grid systems,
Cost, efficiency, and backup comparison,
Key components required,
And how to get government subsidy in India.
How Does a Solar System Work?
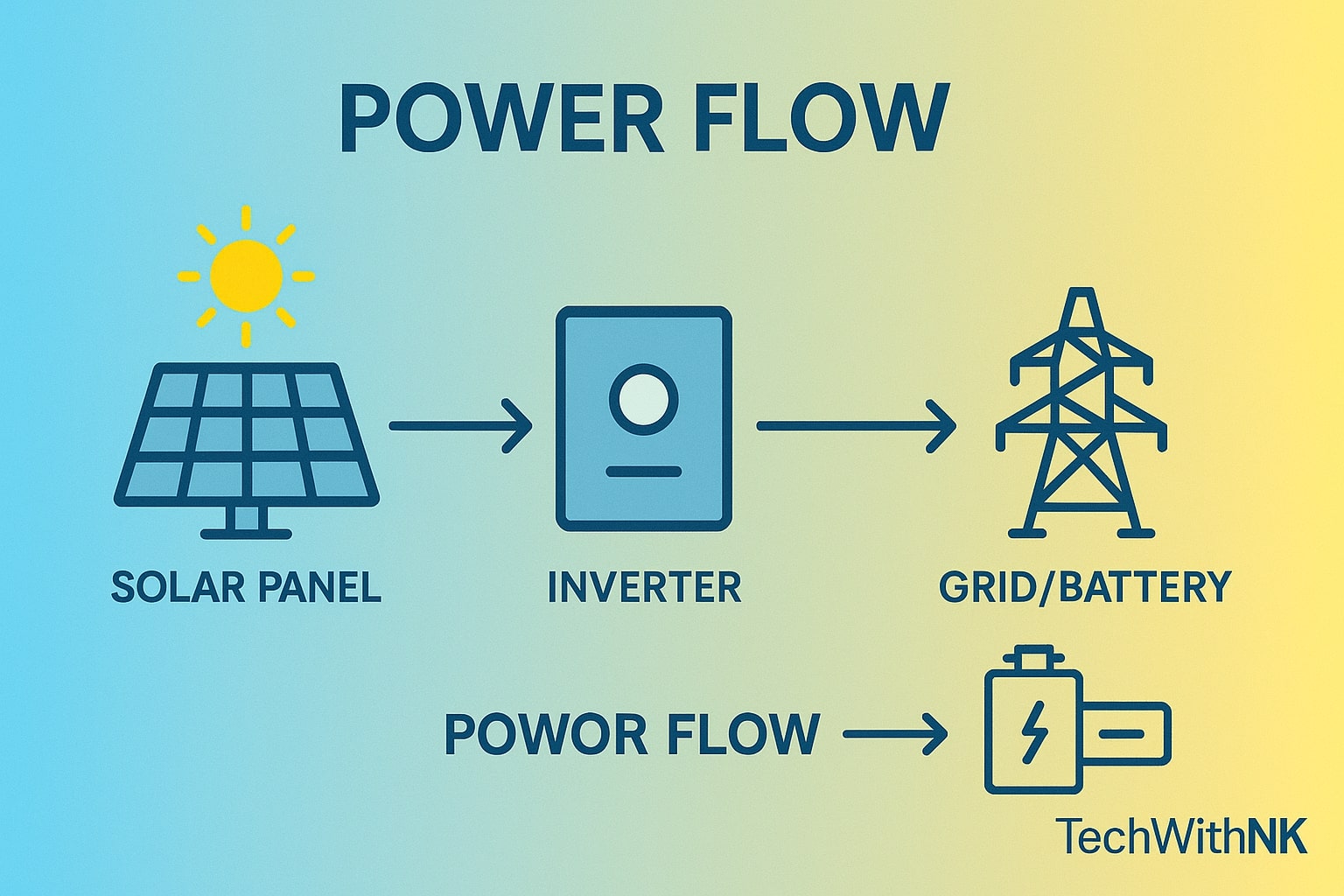
A solar power system converts sunlight into usable electricity through photovoltaic (PV) panels.
⚙️ Working Process:
Solar Panels absorb sunlight and generate DC (Direct Current).
Solar Inverter converts DC into AC (Alternating Current) – usable by household appliances.
Power Distribution:
In on-grid systems, electricity flows to your home and excess is sent to the grid.
In off-grid systems, power charges the battery for backup use.
Types of Solar Power Systems
| Type | Description | Suitable For | Power Backup | Grid Connection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| On-Grid (Grid-Tied) | Connected to the utility grid | Homes with stable electricity supply | ❌ No backup | ✅ Yes |
| Off-Grid (Standalone) | Independent from the grid | Remote/rural areas | ✅ Full backup | ❌ No |
| Hybrid | Combines on-grid + battery backup | Urban homes needing both grid + backup | ✅ Partial/Full | ✅ Y |
On-Grid Solar System – Explained
An on-grid solar system (also called a grid-tied system) is directly connected to the state electricity grid.
🔧 Components:
Solar panels
On-grid inverter (string or micro-inverter)
AC/DC distribution box
Net meter
Mounting structure
🌍 How It Works:
Solar panels generate DC electricity.
Inverter converts it to AC.
Power is first used by home appliances.
Extra energy is exported to the grid via net metering.
✅ Advantages:
Lowest installation cost.
No need for expensive batteries.
Earn credit via net metering (sell excess power).
Ideal for cities with stable electricity supply.
❌ Disadvantages:
No power during grid failure (for safety reasons).
Dependent on DISCOM approval and net meter availability.
Off-Grid Solar System – Explained
An off-grid solar system works independently of the electricity grid. It includes batteries to store excess power for nighttime or cloudy days.
🔧 Components:
Solar panels
Charge controller
Off-grid inverter
Battery bank (Lead-acid or Lithium-ion)
AC/DC distribution box
🌍 How It Works:
Solar panels charge the batteries via a charge controller.
Inverter draws stored power from batteries to supply your home.
System runs completely without grid power.
✅ Advantages:
100% independence from the grid.
Provides power even during outages.
Suitable for remote areas.
❌ Disadvantages:
Higher initial cost (batteries are expensive).
Battery life is limited (4–7 years).
Requires regular maintenance.
Hybrid Solar System – The Best of Both Worlds
A hybrid system combines the benefits of on-grid and off-grid systems. It connects to the grid and includes battery backup.
🔧 Components:
Solar panels
Hybrid inverter
Battery bank
Grid connection
🌍 How It Works:
Solar power runs your home.
Extra power charges the batteries.
Once batteries are full, extra power goes to the grid.
During grid failure, it runs on battery backup.
✅ Advantages:
Backup power during outages.
Earns from net metering.
Smart energy management.
❌ Disadvantages:
High upfront cost.
More complex installation.
Cost Comparison (India 2025)
| System Type | Capacity | Average Cost (₹/kW) | With Battery | Without Battery | Backup | Ideal User |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| On-Grid | 3 kW | ₹55,000–₹65,000 | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | Urban homes |
| Off-Grid | 3 kW | ₹90,000–₹1,10,000 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Rural or remote |
| Hybrid | 3 kW | ₹1,20,000–₹1,40,000 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Premium users |
💡 Note: Prices vary based on brand (Tata, Luminous, Loom Solar, Havells, etc.), battery type, and location.
Battery Options for Off-Grid & Hybrid Systems
| Battery Type | Lifespan | Maintenance | Cost | Efficiency | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | 4–6 years | High | ₹10,000–₹20,000 | 80% | Budget users |
| Lithium-ion | 10–12 years | Low | ₹40,000+ | 95% | Premium users |
Tip: Lithium batteries are expensive but long-lasting and maintenance-free — best for hybrid systems.
Choosing the Right Solar Panel Type
| Panel Type | Efficiency | Cost | Durability | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monocrystalline | 19–22% | High | Long | Small rooftops |
| Polycrystalline | 16–18% | Medium | Moderate | Large rooftops |
| Thin-Film | 10–13% | Low | Low | Portable setups |
Recommendation: For Indian homes, monocrystalline PERC panels are most efficient and future-proof.
How to Choose the Right Solar System for Your Home
Step-by-step:
Check your electricity bill → Note your monthly consumption (in kWh).
Estimate solar capacity:
Required Capacity (kW) = Average Monthly Units ÷ 120
Example: 360 units/month → 360 ÷ 120 = 3 kW systemAssess roof area – ~100 sq.ft per kW.
Decide system type:
Urban area → On-Grid
Rural/off-grid area → Off-Grid
Need backup + net meter → Hybrid
Choose reputed brands (Tata Power Solar, Luminous, Loom Solar, Havells, Microtek).
Apply for MNRE subsidy.
Hire an authorized installer.
Government Subsidy in India (2025)
As per MNRE (Ministry of New and Renewable Energy) guidelines:
| System Capacity | Subsidy (Residential) | Net Meter Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 3 kW | 60% of benchmark cost | ✅ Required |
| 3–10 kW | 40% | ✅ Required |
| Above 10 kW | 20% | ✅ Required |
Apply through: National Portal for Rooftop Solar
Installation & Maintenance Tips
Use south-facing roof for maximum sunlight.
Clean panels every 15–20 days.
Use MC4 connectors for safe wiring.
Keep inverter in a cool, ventilated area.
Install lightning protection and earthing.
Comparison: On-Grid vs Off-Grid vs Hybrid
| Feature | On-Grid | Off-Grid | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grid Connection | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Battery Backup | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Net Metering | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Power During Outage | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Cost | ₹₹ | ₹₹₹ | ₹₹₹₹ |
| Maintenance | Low | High | Medium |
| Ideal For | Urban homes | Remote areas | Premium users |
Smart Features in Modern Solar Systems
IoT-based monitoring via smartphone app.
Smart inverters with Wi-Fi connectivity.
AI-powered energy analytics (in hybrid models).
Zero export systems for restricted DISCOM zones.
Environmental Benefits
Reduces carbon footprint (approx. 1 ton CO₂ saved per kW per year).
Supports sustainable development goals (SDGs).
Reduces dependency on fossil fuels.
Top Solar Panel Brands in India (2025)
| Brand | Type | Warranty | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tata Power Solar | Mono / Poly | 25 Years | India |
| Luminous | Mono | 25 Years | India |
| Loom Solar | Mono PERC | 25 Years | India |
| Havells | Mono | 20 Years | India |
| Adani Solar | Mono / Poly | 25 Years | India |
TechWithNK Recommendation
If you live in an urban or semi-urban area with stable electricity —
👉 Go for an On-Grid System with net metering (lower cost, quick ROI).
If you live in a rural area with frequent outages —
👉 Off-Grid System or Hybrid System is ideal for reliable power.
ROI Tip:
A 3 kW on-grid system pays for itself in 4–5 years and gives free electricity for the next 20 years! ⚡
How much does a 3kW on-grid solar system cost in India (2025)?
👉 Around ₹1.8 lakh before subsidy; ₹1 lakh after subsidy.
Can I run AC and fridge on a 3kW solar system?
✅ Yes, a 3kW system can run 1 AC + fridge + lights + fan.
What happens during power cuts in an on-grid system?
❌ The system shuts down automatically (for safety).