Table of Contents
Toggle🧠 Introduction: The Digital Revolution in Voting
In a democracy as vast as India, ensuring fair and efficient elections is a monumental task. To handle the challenges of manual ballot papers — including counting delays and invalid votes — India adopted the evm machine, or Electronic Voting Machine, a revolutionary step that transformed how millions cast their votes.
The evm machine is a simple yet sophisticated device designed to record votes electronically and eliminate errors associated with paper ballots. It ensures faster counting, transparency, and minimal human interference.
📘 What is an EVM Machine?
(EVM Machine Full Form Explained)
The evm machine full form is Electronic Voting Machine.
It is an electronic device used to record votes during elections instead of traditional ballot papers.
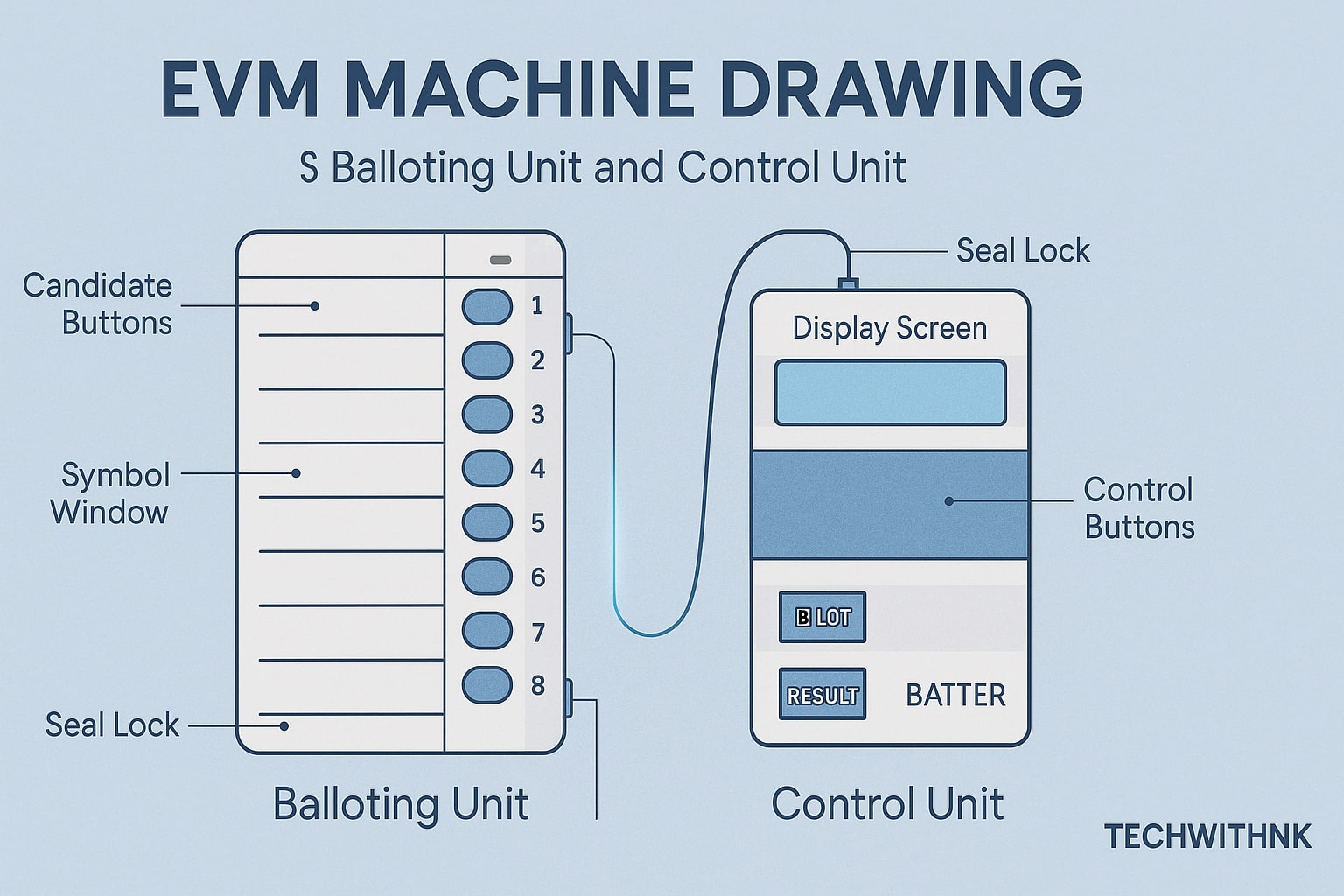
An EVM machine consists of two main units:
Control Unit (CU) – Operated by polling officers.
Balloting Unit (BU) – Used by voters to cast their votes.
Both units are connected by a five-meter cable and work together to ensure accurate vote recording.
⚙️ Components of an EVM Machine
Let’s understand the major parts and their functions in detail:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Balloting Unit (BU) | Contains candidate names and symbols with corresponding blue buttons for voters to press. |
| Control Unit (CU) | Stores the total votes; controlled by the polling officer. |
| Cable Connector | Connects BU and CU securely. |
| Display Screen | Shows number of votes cast and total counts during counting. |
| Battery Pack | Provides portable DC power (works even without electricity). |
| Sealing & Locks | Prevent tampering or reopening after the poll. |
🧩 Internal Working – Step-by-Step Process of How EVM Machine Works
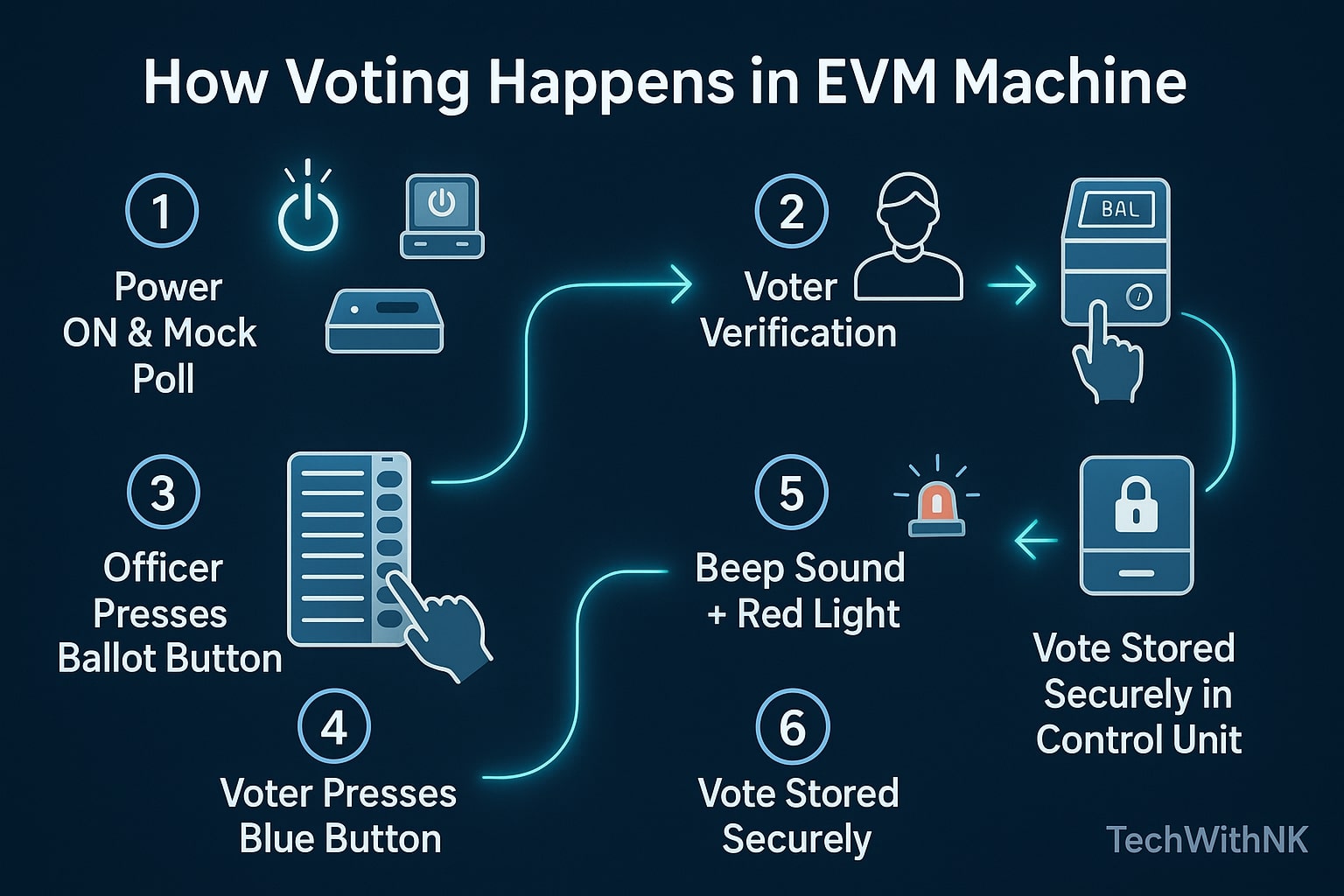
The evm machine is built for simplicity and reliability. Here’s the step-by-step explanation of how it operates during elections:
Power and Initialization
The Control Unit is powered by a sealed battery pack.
Before polling begins, the presiding officer performs a mock poll to verify proper functioning.
Voter Identification
The voter’s name is verified in the electoral roll.
Once confirmed, the officer presses the ‘Ballot’ button on the Control Unit.
Vote Casting
The Balloting Unit becomes active for one vote.
The voter presses the blue button corresponding to their preferred candidate.
A red LED light glows and a beep sound confirms successful voting.
Vote Recording
The information of the chosen candidate is digitally stored in the Control Unit’s memory.
The BU automatically disables after a single vote to prevent multiple entries.
Secure Storage
The Control Unit safely stores votes in non-volatile memory (data remains intact even if power fails).
At the end of the poll, it is sealed and taken to the counting center.
Vote Counting
During counting, the ‘Result’ button on the Control Unit displays votes for each candidate.
No internet or external connection exists, making hacking practically impossible.
EVM machine drawing
⚡ Technical Working Principle
EVMs are based on microcontroller technology that stores digital data securely. Here’s a technical breakdown:
Microcontroller Board: Controls signal processing between BU and CU.
Memory Unit: Stores vote data in binary (digital 0/1).
Beep Circuit: Generates sound feedback upon vote registration.
Display Unit: LCD shows candidate numbers and results.
Battery Module: Supplies regulated DC voltage.
Firmware Lock: Prevents any data overwrite once sealed.
These internal circuits make the evm machine highly secure and tamper-resistant.
🔒 Security Features of EVM Machine
Security is the most crucial factor in elections. EVMs have multiple layers of protection:
Standalone Operation – Not connected to the internet.
Unique ID & Seals – Each machine has a unique serial number and tamper-proof seals.
One Vote at a Time – Prevents multiple votes for one ballot press.
Mock Poll Verification – Conducted before polling starts.
Result Freeze – Data cannot be erased or changed after sealing.
VVPAT Integration – (Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail) shows printed proof to the voter.
No Software Updates – Firmware is permanently written in ROM (cannot be modified).

🧑🔬 Who Invented EVM Machine in World?
The concept of electronic voting dates back decades. However, the first practical EVM machine for official elections was developed in India by two public-sector companies:
Electronics Corporation of India Limited (ECIL), Hyderabad
Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Bengaluru
The design was conceptualized by M.B. Haneefa, an Indian engineer, in the 1980s.
So, if you’re wondering who invented evm machine in world — the credit largely goes to M.B. Haneefa of India, making it a proud innovation in democratic technology.
🌍 EVM Usage in India and Worldwide
In India:
First tested in Kerala, 1982 (Parur Assembly Constituency).
Officially used in all elections since 2004.
Designed to function in extreme weather conditions.
Uses VVPAT since 2014 for extra transparency.
Globally:
Brazil, Philippines, and Estonia also use electronic voting systems.
India’s model stands out for offline operation and non-connectivity to any network, ensuring unmatched security.
🧾 Advantages of EVM Machine
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed | Counting completed within hours. |
| Accuracy | Eliminates invalid or misread votes. |
| Security | Tamper-proof and sealed. |
| Cost-Effective | Saves paper and logistics costs. |
| Eco-Friendly | No paper ballots, no wastage. |
| Accessible | Simple one-button operation even for illiterate voters. |
⚖️ Disadvantages & Criticisms
Though reliable, some concerns are often raised:
Lack of transparency in software code verification.
Need for stronger voter education.
Occasional hardware malfunction (rare but possible).
Dependence on VVPAT for audit verification.
Despite these, India’s evm machine has proven to be a strong and secure system globally recognized for efficiency.
🧰 Maintenance and Testing of EVMs
Before every election:
First-Level Checking (FLC): Conducted by engineers from BEL/ECIL in presence of party representatives.
Mock Polls: Sample votes tested before official use.
Sealing: Once verified, machines are sealed with signatures and stored securely.
Post-Election Audit: Randomly selected EVMs are cross-verified with VVPAT slips.
🧠 Interesting Facts About EVM Machine
Each evm machine can record up to 2,000 votes.
It can list up to 64 candidates (using multiple balloting units).
Weight: Around 5–6 kg, easy to carry in rural areas.
Made in India by BEL and ECIL, under Election Commission supervision.
No Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or network chip — purely standalone.
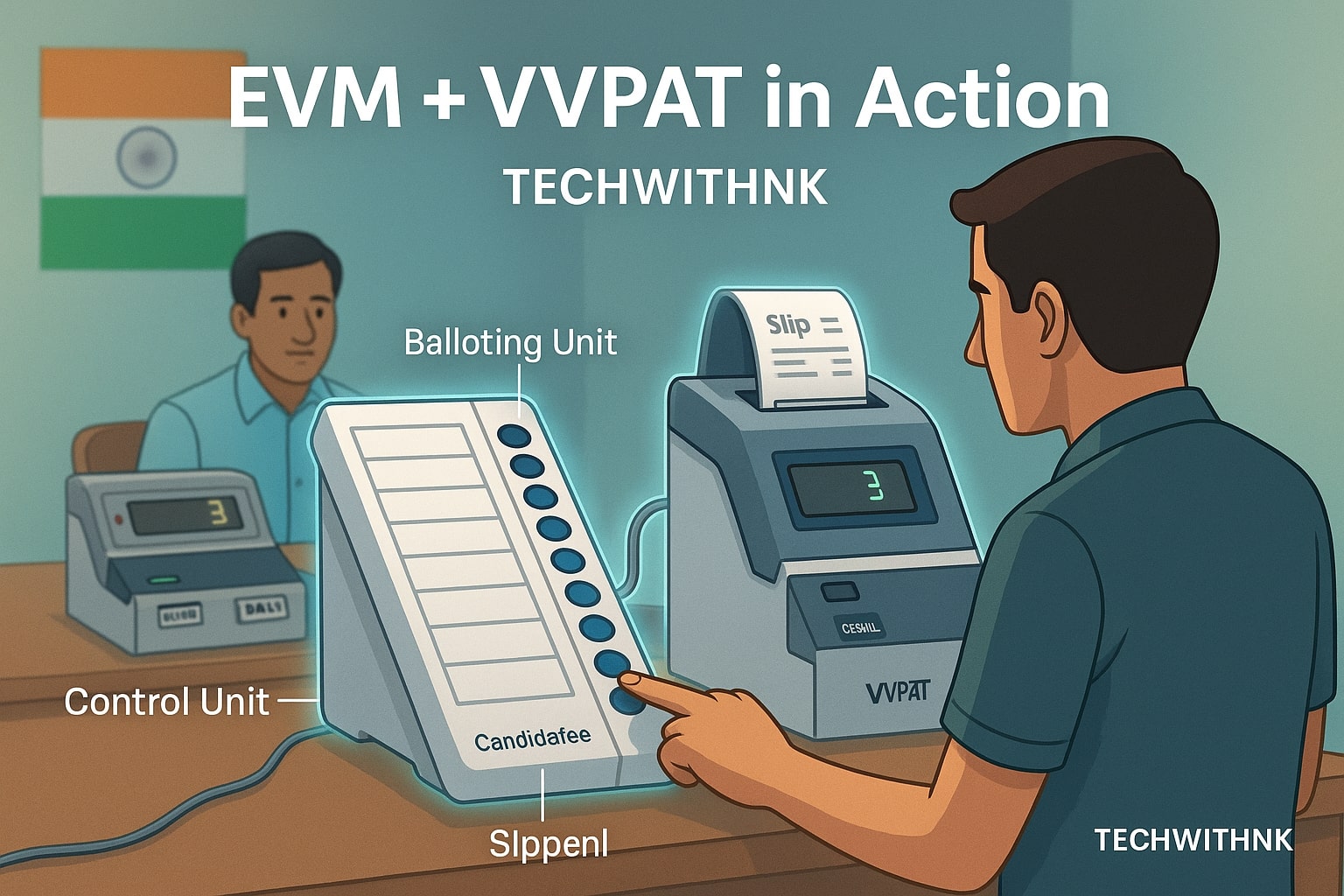
🖨️ VVPAT System – The Paper Trail System
The Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) is an add-on unit attached to the EVM to enhance transparency.
When a voter presses the button:
The chosen candidate’s name and symbol appear on a small screen.
A paper slip prints inside VVPAT (visible for 7 seconds).
The slip falls into a sealed box — ensuring the voter’s choice is verified.
This hybrid approach bridges digital voting with physical verification.
🧾 EVM Machine in Modern Democracy
The evm machine has strengthened democracy by reducing booth capturing, vote invalidation, and delays in counting. It has also increased trust in the Election Commission of India, making large-scale elections manageable, fair, and quick.
India’s success with EVMs has inspired other countries to explore similar systems adapted for their own political frameworks.
🔚 Conclusion
The EVM machine represents India’s commitment to technological advancement and electoral integrity. It combines engineering precision, democratic transparency, and ease of use — ensuring every citizen’s vote counts securely.
From understanding the evm machine full form to exploring who invented evm machine in world, we’ve uncovered how this device transformed voting forever. With ongoing improvements like VVPAT, the EVM continues to stand as a pillar of modern democracy.
What is the EVM machine full form?
The full form of EVM is Electronic Voting Machine.
Who invented the EVM machine in world?
The EVM was conceptualized and developed in India by M.B. Haneefa and manufactured by BEL and ECIL.
How does an EVM machine work?
It records votes electronically via two connected units — a Balloting Unit for the voter and a Control Unit for the officer. Each vote is stored digitally and securely counted.
Can an EVM be hacked?
No. It’s a standalone machine with no internet connectivity, making remote hacking impossible.














