Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Space travel has always depended on powerful rockets—loud, expensive, and difficult to reuse. But a breakthrough concept is now transforming how scientists imagine future missions: the space elevator. For decades, engineers have debated what are space elevators?, are space elevators possible, and how they could reduce the cost of reaching orbit by more than 90%. In this article, you’ll get space elevators explained in a clear, simple, and futuristic way—and learn why they might eventually replace traditional rockets.

What Are Space Elevators?
To put it simply, a space elevator is a giant structure that extends from Earth’s surface all the way to space. Imagine a 36,000 km long cable anchored to the ground on one end, and connected to a counterweight in orbit on the other. Robotic climbers move along the cable carrying cargo, satellites, and possibly humans into space—without using conventional rockets.
This idea might sound like science fiction, but the physics behind it are real. The key is geostationary orbit—a region where an object rotates with Earth, remaining above the same point on the equator. If a cable stretches beyond that point, the counterweight’s centrifugal force keeps the entire system tight, like a stretched guitar string.
So when people ask, what are space elevators?, the simplest answer is:
A tall, cable-based structure that lifts cargo to space using electricity instead of rocket fuel.
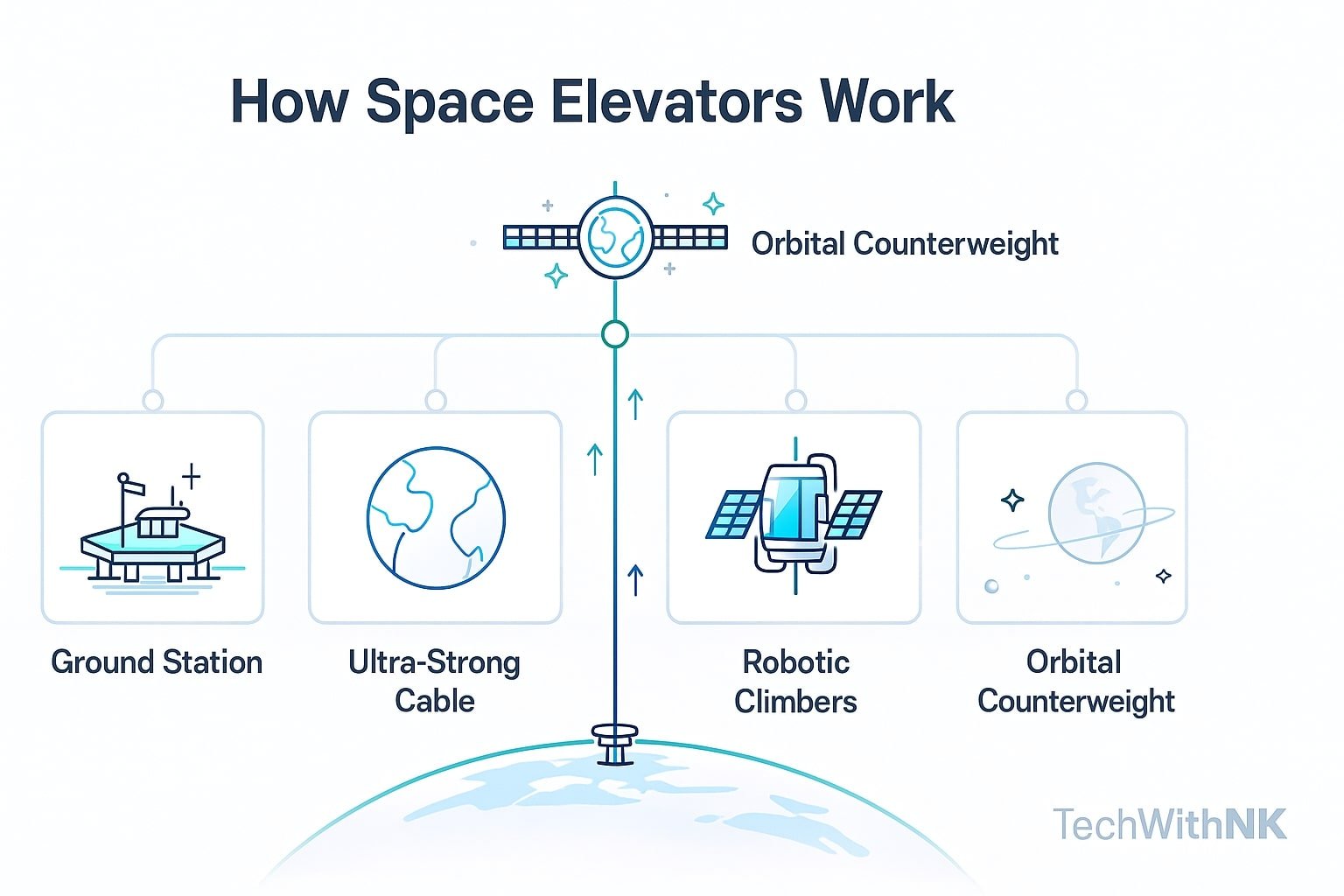
The Major Parts of a Space Elevator (Explained Simply)
To have space elevators explained clearly, here are the main components:
1️⃣ Ground Station
A floating platform or anchored base at the equator. This is where payloads are loaded onto climbers.
2️⃣ Ultra-Strong Cable
This is the hardest part to engineer. The cable needs to be stronger than any building material known today. Scientists propose:
Carbon nanotubes
Graphene materials
Diamond nanothreads
These futuristic materials could support the enormous tension.
3️⃣ Robotic Climbers
Instead of rocket engines, these machines use:
Electric motors
Magnetic rails
Solar-powered drives
Laser-beamed energy
They climb gradually, reaching orbit in a matter of days rather than minutes.
4️⃣ Counterweight in Space
A large mass beyond geostationary orbit that keeps the cable tight due to centrifugal force.
This simple but brilliant structure is what makes the space elevator such a powerful alternative to rockets.
Why Space Elevators Could Replace Rockets
Here’s why scientists believe a space elevator could become the future of space travel:
Massive Cost Reduction
Rockets are expensive because they burn huge amounts of fuel and can be used only once or a few times.
A space elevator uses electricity instead of rocket fuel.
Estimated cost reduction: From $20,000/kg to $200/kg or even lower.
That’s a 99% drop, making space more accessible to:
Universities
Start-ups
Small countries
Private companies
Zero Emissions
Rockets pollute the atmosphere with exhaust and soot.
A space elevator is electrically powered.
If powered by solar energy, space launches could become carbon-neutral.
Continuous Access to Space
Rockets launch occasionally.
A space elevator can run 24/7, like a conveyor belt to orbit.
This allows:
Faster satellite deployment
Cheap space tourism
Continuous cargo supply to space stations
Easy space manufacturing
No Vibrations or Extreme Forces
Astronauts traveling via a space elevator avoid:
3–4 g acceleration
Intense vibrations
Explosive rocket stages
It becomes a smooth, slow ride—similar to taking a high-speed elevator to space.
Safer & More Reliable
Rockets fail sometimes.
Mechanical climbers on a cable face less risk.
Maintenance is also easier because all parts are accessible from the ground

Are Space Elevators Possible Today?
One of the biggest questions people ask is: are space elevators possible with today’s technology?
✔️ The Physics Works Perfectly
Scientists agree: nothing violates physical laws.
❌ But Materials Do Not Exist Yet
The biggest challenge is finding a material strong enough to survive 36,000 km of tension.
Carbon nanotubes are close—but not perfect yet. Researchers believe strong, lightweight materials will be available by 2045–2050.
⚙️ Engineering Challenges
Engineers also need to solve:
Atmospheric storms
Space debris
Lightning strikes
Cable oscillation
Orbital vibrations
None of these problems are impossible—they just require new engineering innovations.
🌐 International Projects
Several organizations are actively working on prototypes:
Obayashi Corporation (Japan)
LiftPort Group
Chinese Academy of Sciences
This makes the idea more realistic than ever before.
How a Space Elevator Would Actually Work
Here’s the complete process, with space elevators explained in the most practical way:
Step 1: Payload Loaded on the Ground
Cargo or humans board the climber at the equator.
Step 2: Electric Climber Ascends
The climber uses:
Solar energy
Ground-based laser beams
Batteries
Magnetic propulsion
It slowly climbs the cable.
Step 3: Reaches Orbit
At geostationary orbit, the climber unloads materials into:
Space stations
Satellites
Orbital factories
Step 4: Emergency Escape Pod
Humans can descend through gravity, similar to an elevator counterweight system.
Step 5: Space-to-Moon Elevator
Once Earth becomes easy to access, a second elevator could extend from the Moon—making lunar transport almost free.
What a Post-Rocket World Could Look Like
Imagine life when space elevators become everyday tools:
Satellites launched daily like courier packages
Factories in orbit producing semiconductors or medicines
Moon mining made profitable
Space tourism becoming cheaper than airplane travel
100% clean, green space access for everyone
Rockets will still be used for deep space missions, but most Earth-to-orbit missions will shift to elevators.
It’s a revolution waiting to happen.
Conclusion: A Future Built on the Space Elevator
So now you have space elevators explained in detail. The space elevator is not just a wild futuristic idea—it’s a transformative solution to make space travel cheaper, safer, and sustainable. Today, we are still developing the materials needed to build it, but once completed, it could fully change how humanity interacts with space.
When people ask, are space elevators possible?—the answer is clear:
Yes, not today—but very soon. And once built, they may finally replace rockets as the main gateway to space.