Table of Contents
Toggle🇮🇳 India’s Renewable Energy Journey – Solar Parks and Hydrogen Hubs
A Deep Dive into India’s Clean Energy Revolution and Its Future Potential
(By TechWithNK – 2025 Edition)
🌞 Introduction: India’s Race Toward a Clean Energy Future
India is rapidly transitioning toward a sustainable future by expanding renewable energy in India through solar parks, wind farms, and emerging hydrogen energy hubs. These diverse renewable energy resources are reshaping the nation’s power landscape.
India is standing at a historic energy crossroads. With its growing economy, massive population, and rising electricity demand, the country faces one of the toughest challenges of our time — how to fuel development without fueling pollution.
The answer lies in renewable energy — particularly solar power and the emerging frontier of green hydrogen. Over the past decade, India has transformed from a coal-dependent nation into a global leader in clean energy installations.
From the world’s largest solar parks in Rajasthan and Gujarat to the ambitious National Green Hydrogen Mission, India’s journey represents innovation, resilience, and a commitment to sustainable growth.
⚡ The Renewable Energy In India in Numbers
Let’s start with some perspective:renewable energy in India in MW
| Metric | Status (2025) | Target (2030) |
|---|---|---|
| Installed Renewable Capacity | ~185 GW | 500 GW |
| Solar Energy | ~80 GW | 280 GW |
| Wind Energy | ~46 GW | 140 GW |
| Hydropower | ~47 GW | 70 GW |
| Bioenergy | ~12 GW | 25 GW |
| Green Hydrogen Production | 0.1 MTPA (pilot stage) | 5 MTPA |
India is the 3rd largest renewable energy producer in the world (after China and the USA), and aims to meet 50% of its total energy demand from renewables by 2030.
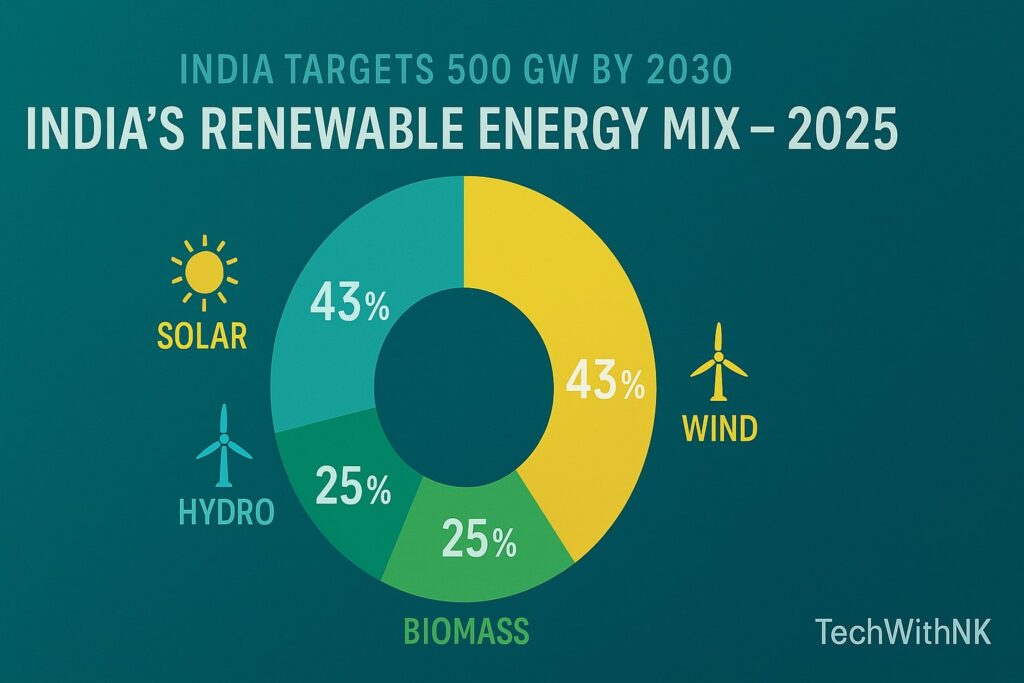
Solar Parks In India: Key Pillars of Renewable Energy in India
1. Why Solar Energy Is Key for India
Abundant sunlight: 300+ sunny days per year.
Falling solar costs: Module prices dropped over 85% in a decade.
Scalability: From rooftop panels to 5,000-acre mega-parks.
Employment: Over 1 million jobs expected by 2030 in solar sector.
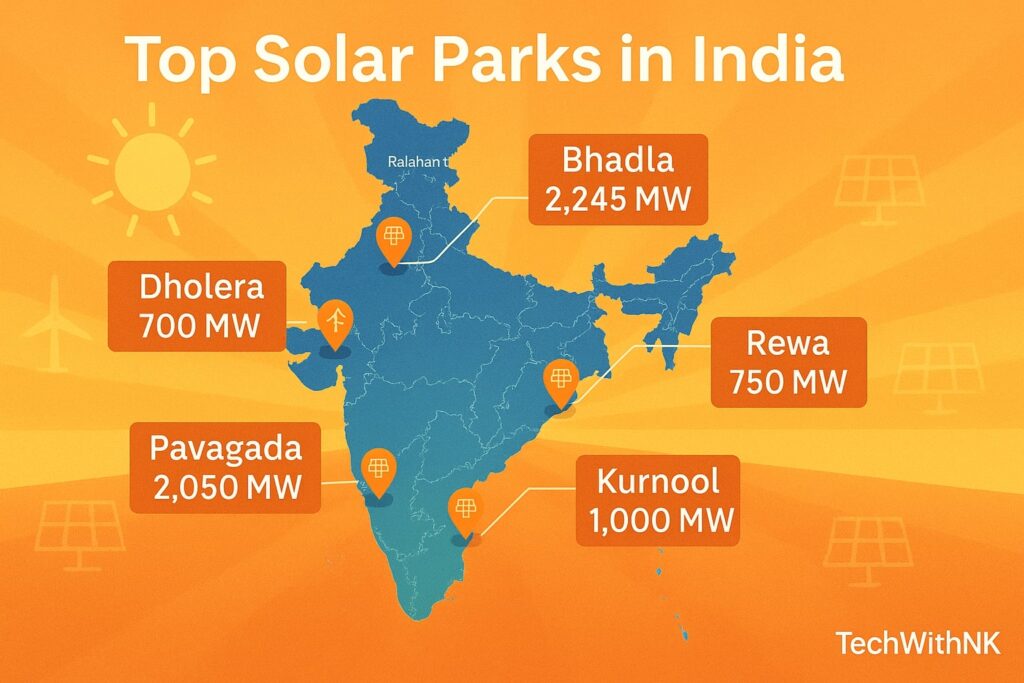
2. India’s Mega Solar Parks
India’s strategy focuses on ultra-mega solar parks — massive clusters of solar farms built in high-radiation areas.
| Solar Park | Location | Capacity (MW) | Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bhadla Solar Park | Rajasthan | 2,245 | World’s largest; covers 14,000 acres |
| Pavagada Solar Park | Karnataka | 2,050 | Built on leased farmland |
| Rewa Ultra Mega Solar Park | Madhya Pradesh | 750 | Supplies Delhi Metro |
| Kurnool Ultra Mega Solar Park | Andhra Pradesh | 1,000 | Fully operational since 2017 |
| Dholera Solar Park | Gujarat | 5,000 (under development) | India’s biggest upcoming solar park |
🔆 Fun fact: The Bhadla Solar Park is so vast that it’s visible from space, producing more than 6 million units of electricity daily.
3. Rooftop Solar – Powering Homes and Cities
India aims for 40 GW rooftop solar capacity, promoting decentralized energy generation.
Government initiatives like PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana (2024) offer subsidies up to 60% for residential rooftop systems, making clean power accessible to every household.
🌬️ Beyond Solar – Wind, Hydro, and Biomass
While solar leads, India’s energy diversity ensures resilience:
Wind Energy: Strong potential in Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, and Maharashtra; hybrid wind-solar parks are emerging.
Hydropower: North-eastern states and the Himalayas drive sustainable dam projects.
Biomass & Biogas: Converting crop residues and municipal waste into energy — reducing air pollution and supporting rural income.
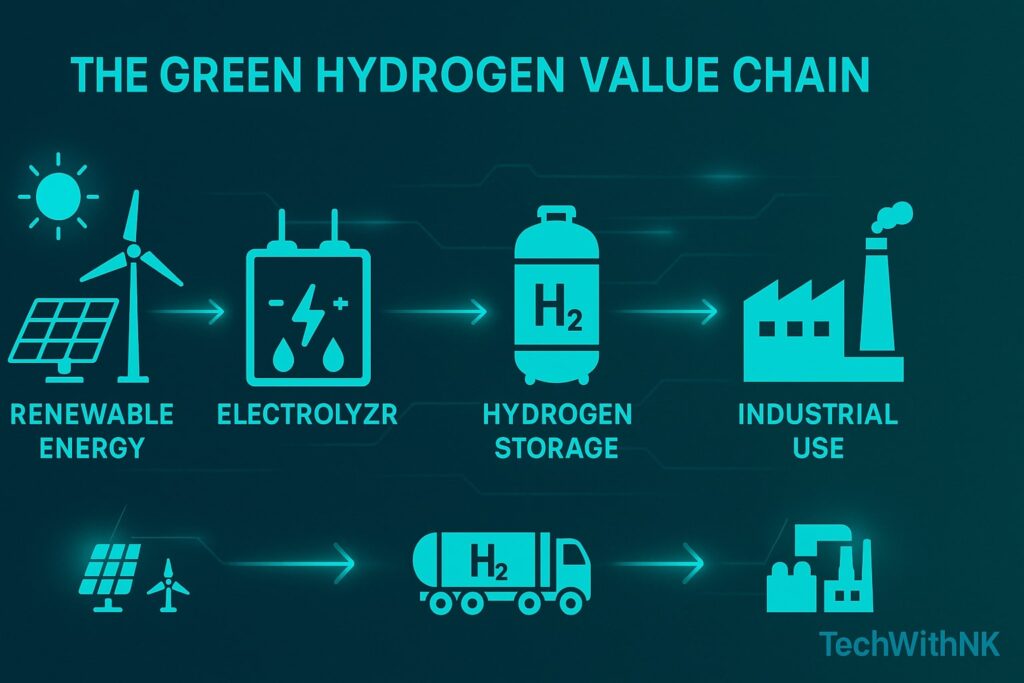
🧪 The Hydrogen Revolution – Powering the Next Generation
Green hydrogen is becoming one of India’s most strategic renewable energy resources, connecting solar, wind, and fuel technologies.
1. What Is Green Hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is produced by splitting water (H₂O) into hydrogen and oxygen using renewable electricity (from solar or wind).
It emits zero carbon, unlike grey or blue hydrogen made from fossil fuels.
2. India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission
Launched in 2023, this ₹19,744 crore mission aims to:
Produce 5 million tonnes of green hydrogen annually by 2030
Add 125 GW renewable capacity dedicated to hydrogen production
Create 600,000 jobs
Reduce 50 MMT of CO₂ emissions per year
Enable export potential worth ₹8 lakh crore (~$100 billion)
3. Hydrogen Hubs In India – India’s New Clean Energy Clusters
| Hydrogen Hub | State | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Gujarat (Kandla & Hazira) | Gujarat | Port-based hydrogen & ammonia export |
| Tuticorin Hub | Tamil Nadu | Green hydrogen for fertilizers & shipping |
| Ladakh Hydrogen Valley | Ladakh | Solar-hydrogen integration in high altitude |
| Vizag Hydrogen Hub | Andhra Pradesh | Refinery decarbonization & mobility |
| Mangalore Hydrogen Corridor | Karnataka | Industrial hydrogen use & transport |
These hubs will anchor electrolyzer manufacturing, storage infrastructure, and green ammonia exports, making India a global hydrogen exporter.
⚡ India’s Renewable Energy Resources at a Glance
ndia’s renewable energy resources include solar, wind, biomass, small hydro, and green hydrogen. The government’s ambitious mission aims to achieve over 500 GW of non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030, making renewable energy in India a global model for sustainable growth.
🔋 Green Hydrogen Applications
| Sector | Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | Replacing coking coal in blast furnaces | Zero-carbon steel |
| Fertilizers | Ammonia production | Decarbonized agriculture |
| Refineries | Fuel desulfurization | Cleaner fuels |
| Transport | Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles | Long-range zero-emission transport |
| Power Storage | Seasonal energy storage | Grid stability |
🚗 India’s first hydrogen-powered fuel cell bus was launched by IndianOil in 2024 — a glimpse of the future of zero-emission mobility.
🏭 Major Players in India’s Renewable Energy & Hydrogen Space
| Company | Sector | Key Projects |
|---|---|---|
| Adani Green Energy Ltd. | Solar & Wind | 45 GW target by 2030; Khavda Solar Park |
| Tata Power Renewable | Solar Rooftop & EV | Large-scale rooftop solar networks |
| ReNew Power | Wind, Solar, Hydrogen | Pilot hydrogen project with Larsen & Toubro |
| NTPC Green Energy Ltd. | Hydrogen & Solar | Green hydrogen fueling stations |
| Reliance Industries | Green Hydrogen | Dhirubhai Ambani Green Energy Giga Complex, Jamnagar |
| IndianOil | Hydrogen & Mobility | Hydrogen buses, refinery decarbonization |
| Larsen & Toubro (L&T) | Electrolyzers & Engineering | Hydrogen plants in Gujarat & Oman |
🌍 International Collaborations
India’s renewable journey is supported by global partnerships:
🇫🇷 India–France Solar Alliance (ISA) – joint projects in Africa and Asia.
🇦🇺 India–Australia Hydrogen Alliance – technology sharing for electrolyzers.
🇩🇪 India–Germany Green Energy Corridor – grid modernization and hydrogen hubs.
🇯🇵 India–Japan Energy Transition Pact (2024) – $5 billion investment in hydrogen infrastructure.
🏗️ Policy Framework Driving the Revolution
Key Government Initiatives
National Solar Mission (2010): Foundation of India’s solar push.
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) for Solar Manufacturing: Boosts domestic PV and battery production.
Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO): Mandates utilities to buy green power.
Hydrogen Mission (2023): Focused incentives for hydrogen production and use.
Green Energy Open Access Rules (2022): Easier for industries to buy renewable energy directly.
PM-KUSUM Scheme: Empowers farmers with solar irrigation pumps.
🧭 Challenges Ahead
Despite progress, India faces hurdles in scaling renewables:
Land acquisition and transmission bottlenecks
Intermittent solar/wind generation
Storage costs and limited battery manufacturing
Need for skilled manpower in hydrogen technologies
Policy clarity and financing mechanisms for small players
But with consistent policy support and private-public collaboration, India is poised to overcome these challenges.
🌱 Future Vision: 2040 and Beyond
By 2040, India aims to become a net-zero carbon nation with a green energy economy powered by solar parks, wind farms, and hydrogen hubs.
Expected milestones:
1,000+ GW of renewable capacity
10 million green jobs
Full electrification of transport via EVs & hydrogen fuel cells
India as global exporter of green hydrogen and ammonia
This isn’t just an energy transition — it’s an economic transformation.
📊 Key Takeaways
✅ India is the world’s fastest-growing renewable market
✅ Solar parks like Bhadla and Dholera symbolize large-scale innovation
✅ Hydrogen hubs mark the next big leap in clean energy
✅ Government & industry synergy is crucial for sustainability
✅ Green hydrogen could become “the oil of the future” for India
🧭 Conclusion
India’s renewable energy journey is not merely about reducing emissions — it’s about reshaping the nation’s destiny. With the sun shining on its deserts and hydrogen bubbling in its labs, India is scripting a new chapter in global energy leadership.
From solar parks that power cities to hydrogen hubs that power industries, India is proving that economic growth and environmental protection can go hand in hand.
“The energy of tomorrow is being built today — and India is leading the charge.”
— TechWithNK
What is the target of India’s renewable energy by 2030?
India aims to install 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030, covering solar, wind, hydro, and biomass sources.
Which is the largest solar park in India?
The Bhadla Solar Park in Rajasthan is the world’s largest, with over 2,245 MW capacity spread across 14,000 acres.
What is green hydrogen and why is it important?
Green hydrogen is produced using renewable power through electrolysis of water. It emits zero carbon and can replace fossil fuels in heavy industries and transport.
What are the major renewable energy resources in India?
The major renewable energy resources in India include solar, wind, biomass, hydro, and hydrogen. These sources power millions of homes and industries while reducing carbon emissions.














