Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is one of the core pillars of modern technology. From the smartphone in your pocket to the massive power plants lighting up entire cities, electrical engineering lies at the heart of it all. It combines physics, mathematics, and innovation to design, develop, and maintain systems that generate, transmit, and utilize electrical energy efficiently.
This blog provides a comprehensive guide (6000+ words) to electrical engineering — covering its basics, key principles, branches, applications, and future trends. Whether you’re a student, an aspiring engineer, or just curious about how electricity powers our world, this article will give you the foundation you need.
What is Electrical Engineering?
Definition
Electrical engineering is the study, design, and application of systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It involves everything from small circuits in microprocessors to massive power grids.
A Brief History
19th Century Foundations: Michael Faraday’s experiments with electromagnetic induction, Ohm’s Law (1827), and James Clerk Maxwell’s electromagnetic theory laid the foundation.
20th Century Growth: With the invention of semiconductors, radio, and computers, electrical engineering split into subfields like power engineering, electronics, control systems, and telecommunications.
Today: It integrates with computer science, AI, renewable energy, and nanotechnology.
Basic Concepts in Electrical Engineering
To understand EE, you must first master the fundamental laws and quantities.
1. Electric Charge (Q)
Unit: Coulomb (C)
Carriers: electrons (negative), protons (positive).
2. Electric Current (I)
Flow of charge per unit time.
Formula:
I=QtI = \frac{Q}{t}I=tQUnit: Ampere (A).
3. Voltage (V)
Potential difference between two points.
Unit: Volt (V).
4. Resistance (R)
Opposition to current flow.
Ohm’s Law:
V=I×RV = I \times RV=I×R
5. Power (P)
Rate of energy transfer.
Formula:
P=V×IP = V \times IP=V×I
6. Energy (E)
Electrical energy consumed:
E=P×tE = P \times tE=P×t
Ohm’s Law and Circuit Fundamentals
Ohm’s Law is the backbone of circuit analysis.
Formula: V=I×RV = I \times RV=I×R
Example: If a 12V battery is connected across a 6Ω resistor, current = 2A.
Series Circuits
Rtotal=R1+R2+R3…R_{total} = R_1 + R_2 + R_3 …Rtotal=R1+R2+R3…
Same current flows through all elements.
Parallel Circuits
1Rtotal=1R1+1R2…\frac{1}{R_{total}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} …Rtotal1=R11+R21…
Voltage remains same across branches.
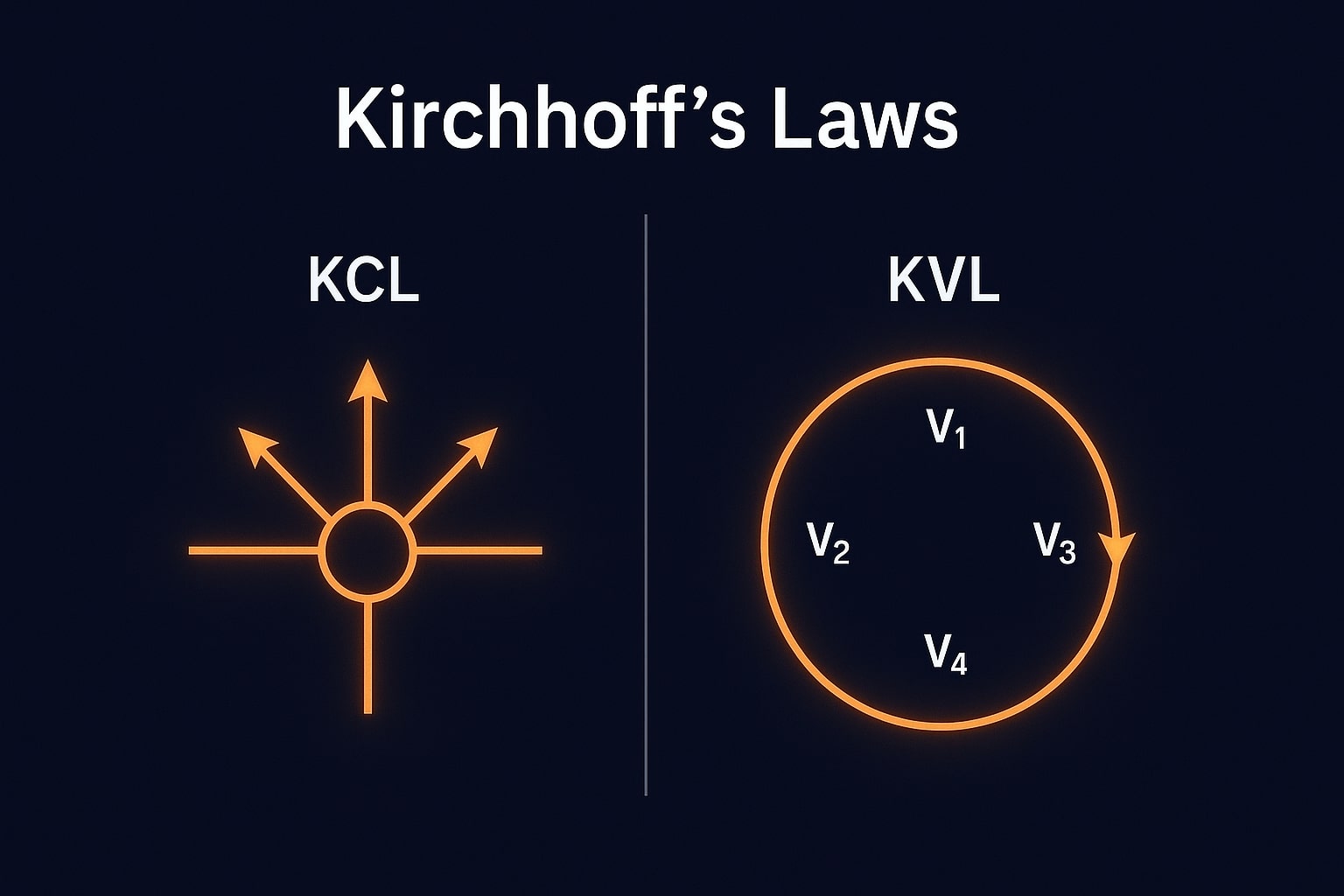
Kirchhoff’s Laws
KCL: Sum of currents entering a node = sum leaving.
KVL: Sum of voltages around a loop = 0.
Major Branches of Electrical Engineering
1. Power Engineering
Focus: generation, transmission, distribution.
Examples: Thermal power plants, solar farms, smart grids.
2. Electronics
Deals with semiconductors, transistors, ICs.
Applications: Smartphones, computers, robotics.
3. Control Systems
Ensures stable, desired output in systems.
Applications: Aircraft autopilots, industrial automation.
4. Telecommunications
Deals with data transmission (wired & wireless).
Examples: Mobile networks, satellite communication.
5. Instrumentation & Measurement
Precision devices to measure electrical/non-electrical quantities.
Applications of Electrical Engineering
1. Power Generation & Distribution
Electricity from coal, hydro, solar, wind, nuclear.
Transmission through high-voltage lines.
2. Electronics in Everyday Life
TVs, computers, medical devices, automation systems.
3. Communication Systems
Mobile phones, internet, radar, GPS.
4. Renewable Energy
Solar panels, wind turbines, hydrogen fuel cells.
5. Emerging Areas
Smart grids, IoT devices, electric vehicles, AI-powered electronics.
Real-World Case Studies
India’s Smart Grid Mission
Uses IoT, AI, and advanced metering for efficient power use.
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Example: Tesla & Tata EVs — use advanced power electronics and battery management.
Communication Revolution
From 2G → 5G, now moving to 6G with low latency and massive connectivity.
Tools and Software in Electrical Engineering
MATLAB / Simulink – modeling and simulations.
AutoCAD Electrical – circuit diagrams.
PSpice – electronic circuit analysis.
ETAP – power system analysis.
Future of Electrical Engineering
AI + Electrical Systems: Predictive maintenance in grids.
Quantum Electronics: Future computing.
Renewables + Storage: Green power revolution.
Nanotechnology: Ultra-small efficient circuits.
Career Opportunities
Power plant engineer
Electronics design engineer
Telecom engineer
Embedded systems developer
Research scientist in AI-electronics
What is the difference between electrical and electronics engineering?
Electrical deals with large-scale power systems; electronics focuses on small-scale devices.
Why is Ohm’s Law important?
It helps analyze how voltage, current, and resistance interact in circuits.
hat is the scope of electrical engineering in India?
Huge demand in renewables, smart grids, EVs, IT, telecom.