Table of Contents
Toggle🌟 Introduction: A New Era of Computing Has Begun
For decades, engineers have pushed the limits of silicon-based computing. Faster CPUs, quantum processors, AI accelerators—each generation gets smaller, faster, and more powerful.
But we are reaching a physical limit. As transistors approach atomic scale, heat dissipation and energy consumption become major barriers.
This is where Biocomputers come in.
Instead of relying on silicon, Biocomputers use human brain cells to process data, mimicking the way real neurons learn, store information, and solve problems. And yes—if you’re wondering “are biocomputers real?”—the answer is yes. Several global labs have already demonstrated working prototypes.
This blog explores what are biocomputers, how they work, why scientists are excited, and what the future might look like.
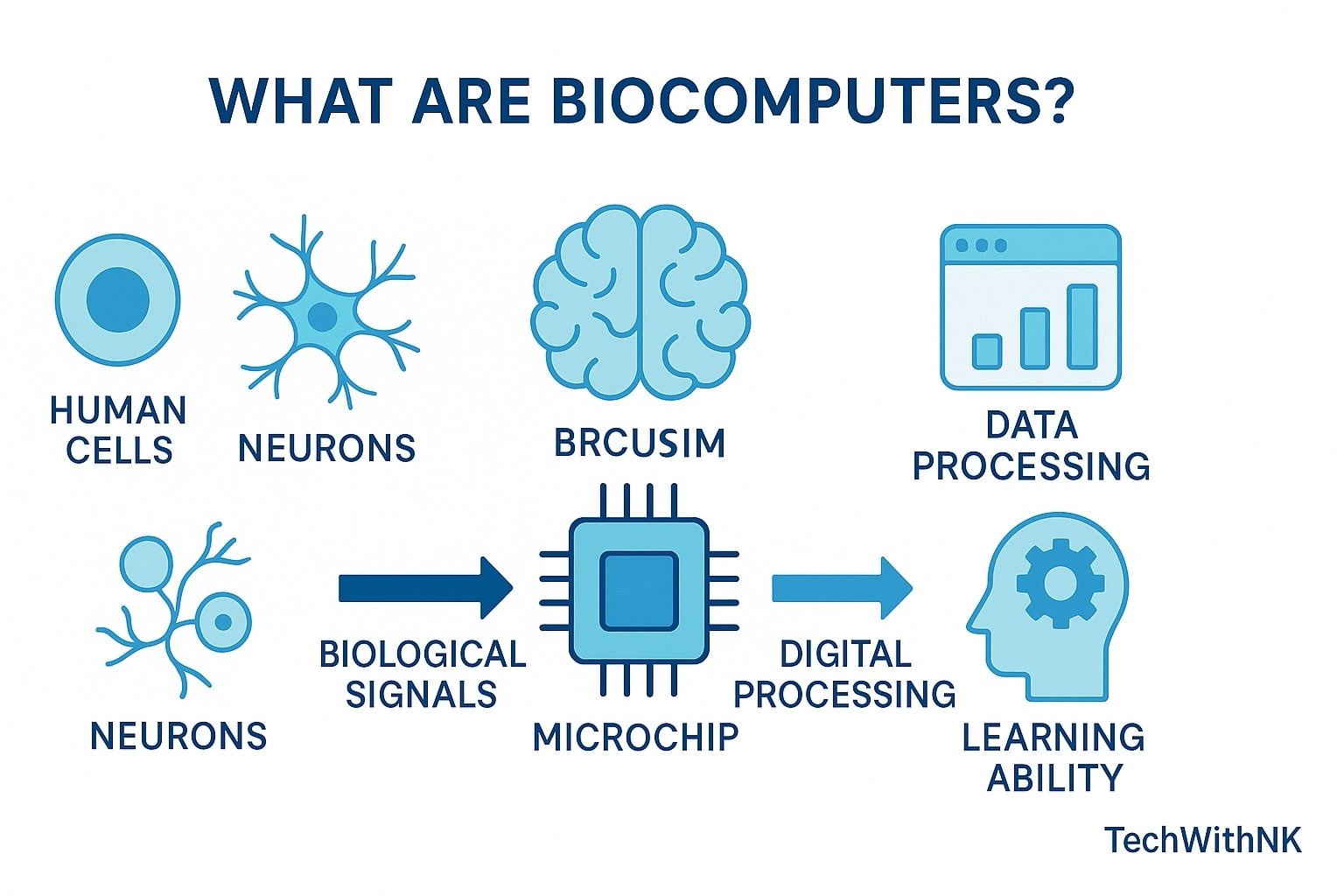
🔬 What Are Biocomputers?
A Biocomputer is a computing system built using biological components such as:
Human brain cells
Neurons grown in a lab
Organ-on-chip technology
Programmable living cells
Instead of electrical circuits, they process information using biological signals, just like a living brain.
In 2023, researchers developed DishBrain, the world’s first system where human neurons learned to play Pong. This showed that human brain cells power biocomputers in ways traditional machines cannot.
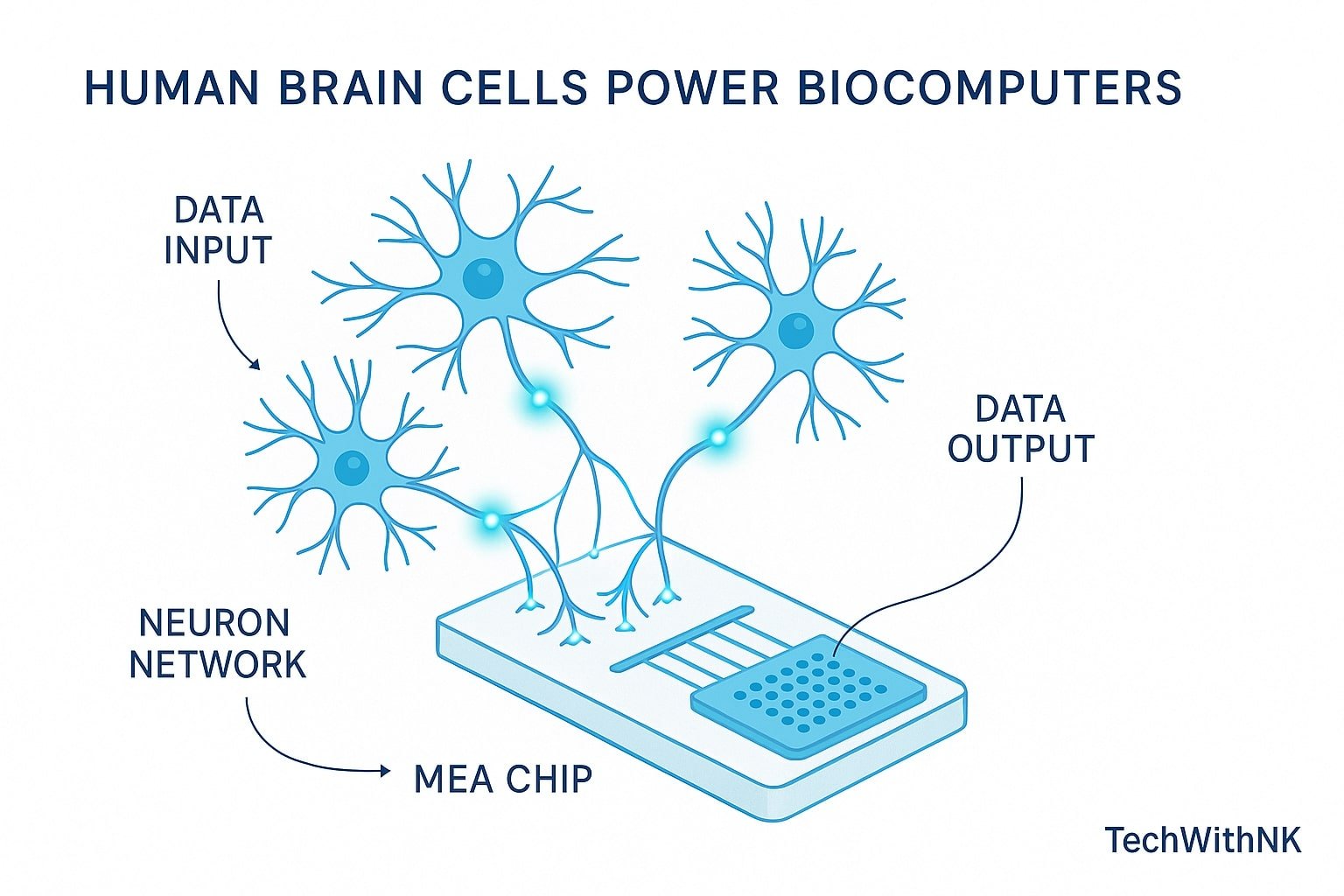
How Human Brain Cells Power Biocomputers
Human neurons are incredibly powerful:
A single brain has 86 billion neurons
Each neuron forms 10,000+ connections
Neural communication is parallel, not sequential
Learning is built into the structure itself
When neurons are placed on a microelectrode array, they:
Form networks
Learn from patterns
Respond to electrical stimulation
Adapt long-term behavior
These abilities make them ideal for adaptive, intelligent computing.
This is why projects on programmable single-cell mammalian biocomputers are gaining global attention. Scientists can now control individual living cells to perform logic operations, store information, and behave like computational circuits.
Why Biocomputers Are the Future
1️⃣ Ultra-Low Energy Consumption
Human neurons use far less energy than silicon chips. The brain runs on 20 watts, while supercomputers consume millions of watts.
2️⃣ Incredible Learning Ability
Biological neurons improve continuously. They don’t need explicit programming—they learn.
3️⃣ Massive Parallelism
While silicon processors handle tasks in series, biological networks handle thousands of tasks at once.
4️⃣ Self-Repair
Unlike silicon, biological systems can regenerate connections.
5️⃣ True Intelligence
Biological systems can display creativity, intuition, and abstraction.
Inside a Biocomputer: How It Actually Works
A modern Biocomputer consists of:
📌 1. Human Neurons
Grown from stem cells, reprogrammed skin cells, or donated tissue.
📌 2. Microelectrode Array (MEA)
A chip that gives electrical input and reads output from the neurons.
📌 3. AI Learning Layer
Connects biological behavior with machine control.
📌 4. Fluid & Nutrient System
Keeps the cells alive and functioning.
📌 5. Software Interface
Translates neural patterns into digital commands.
Real-Life Example: Neurons Learning to Play Computer Games
In a groundbreaking experiment:
Human neurons were exposed to a virtual Pong environment
As the neurons received feedback, they adapted
Within minutes, they learned how to “play” Pong
This shows that Biocomputers can learn behavior, not just follow instructions.

Are Biocomputers Real? Current Projects Worldwide
Yes. Here are the major breakthroughs:
🟦 1. Cortical Labs – DishBrain
Human neurons on a chip controlling a computer environment.
🟦 2. MIT – Biological Logic Gates
Designing decision-making circuits inside living cells.
🟦 3. NIH – Programmable Single-cell Mammalian Biocomputers
Cells programmed like tiny computers using CRISPR.
🟦 4. Stanford – Brain-on-a-chip Models
Used for AI training and neurological research.
🟦 5. ETH Zurich – Biohybrid Computing
Merging silicon and living cells.
Biocomputers have moved from science fiction to active research labs
Biocomputers vs Traditional Computers
| Feature | Biocomputers | Silicon Computers |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Neurons & cells | Transistors |
| Energy Use | Extremely low | High |
| Learning Ability | Natural, adaptive | Pre-programmed |
| Speed | Parallel | Sequential |
| Repair | Self-repairing | No self-repair |
| Intelligence | Biological | Artificial |
Potential Applications of Biocomputers
1. AI Training & Modeling
Brain-like systems for next-generation AI.
2. Drug Discovery
Test medicines on real biological networks.
3. Robotics
Biologically adaptive robots.
4. Disease Research
Study neurological disorders with living neural networks.
5. Cybersecurity
Use unpredictable biological patterns for encryption.
6. Brain-Computer Interfaces
Linking machines and biological systems seamlessly.
Future of Biocomputers: What’s Coming Next?
Scientists predict:
🔹 Biohybrid AI
Combining AI models with living neurons.
🔹 Human-in-the-loop Computing
Neural networks trained with real biological signals.
🔹 Full-Scale Living Processors
Chips that grow, evolve, and repair themselves.
🔹 Synthetic Brains for Machines
Artificial brains made of engineered cells.
🔹 Personalized Biocomputers
Your own cells powering your personal mini-computer.
The field is accelerating fast, and the next decade will redefine computing.
Conclusion
Biocomputers represent one of the most revolutionary shifts in technology. By combining human brain cells with advanced engineering, scientists are creating computing systems capable of:
Learning
Adapting
Evolving
Consuming extremely low energy
With advances in programmable single-cell mammalian biocomputers, synthetic neurons, and organoid intelligence, the future belongs to biological computing.
The rise of Biocomputers is not just an innovation—it is the beginning of a new era where biology and technology merge into one.