Table of Contents
Toggle🌍 Introduction: What Is Weather Radar?
The term weather radar refers to a specialized radar system designed to detect and track precipitation such as rain, snow, hail, or storms in the atmosphere. It sends out radio waves that bounce off water droplets or ice particles, allowing meteorologists to visualize real-time weather conditions.
A live weather radar provides continuous updates that help forecast rainfall, track severe storms, and issue warnings before natural disasters occur. In simple terms, a weather radar acts as the eye of the sky, scanning clouds to reveal where and how intense the precipitation is.
Today, from your smartphone weather apps to complex meteorological centers, weather radar technology has become the backbone of modern weather forecasting systems.
⚙️ How Weather Radar Works
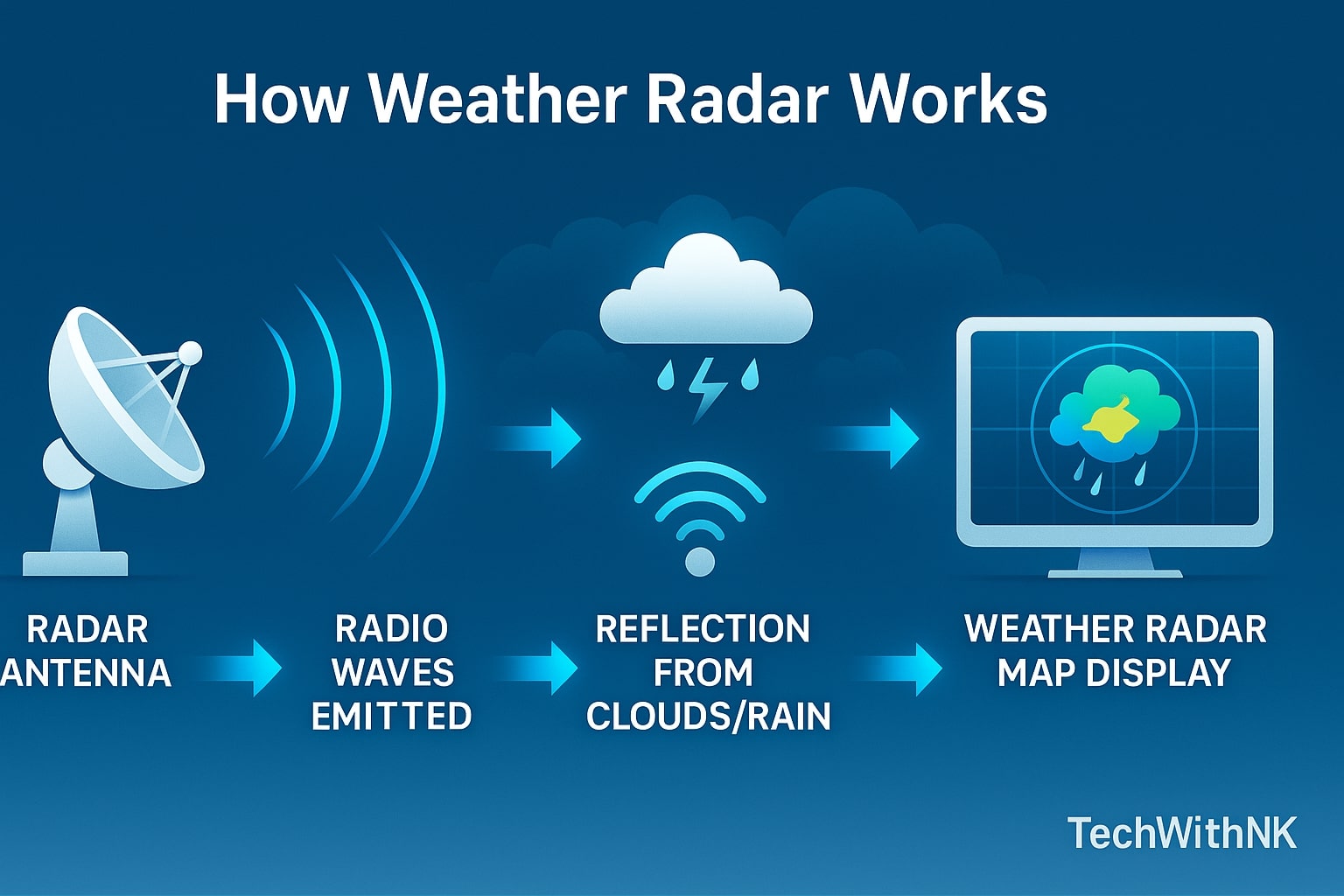
To understand how weather radar works, let’s break it down into simple steps:
Transmission of Radio Waves
The radar emits electromagnetic waves toward the atmosphere using a rotating antenna.Reflection (Echo) from Particles
When these waves encounter raindrops, snowflakes, or hailstones, part of the energy bounces back (echo) toward the radar receiver.Signal Processing
The radar measures how much time the signal takes to return and how strong it is. This helps determine both the distance and intensity of precipitation.Visualization
The processed data is displayed as a weather radar map—typically using color codes to represent different precipitation intensities (e.g., light rain = green, heavy rain = red).
Essentially, weather radar technology converts invisible radio signals into visual images that forecasters can interpret easily. These maps help predict where rain will move next and how severe it may become.
🌪️ Doppler Weather Radar – The Game Changer
Traditional radars could detect only the presence and intensity of rain. However, Doppler weather radar revolutionized meteorology by detecting the motion of precipitation particles.
By measuring changes in the frequency of returned radar waves (the Doppler effect), meteorologists can determine wind speed and direction within a storm. This capability is crucial for identifying:
Tornado formation
Cyclone wind patterns
Thunderstorm rotation
Doppler systems make live weather radar more accurate, enabling early warnings for severe weather events and saving countless lives.
🛰️ Weather Radar Technology Explained
Modern weather radar technology has evolved beyond rotating dishes. It now integrates dual-polarization radar, satellite networks, and AI-based algorithms.
Key advancements include:
Dual-Polarization Radar (Dual-Pol): Sends both horizontal and vertical pulses, improving the identification of precipitation type (rain, snow, hail).
Phased-Array Radar: Scans large areas faster than conventional systems.
Machine Learning Algorithms: Analyze vast radar data for better forecasting accuracy.
These innovations have made weather radar applications more powerful, from national weather services to local apps showing live weather radar imagery in real time.
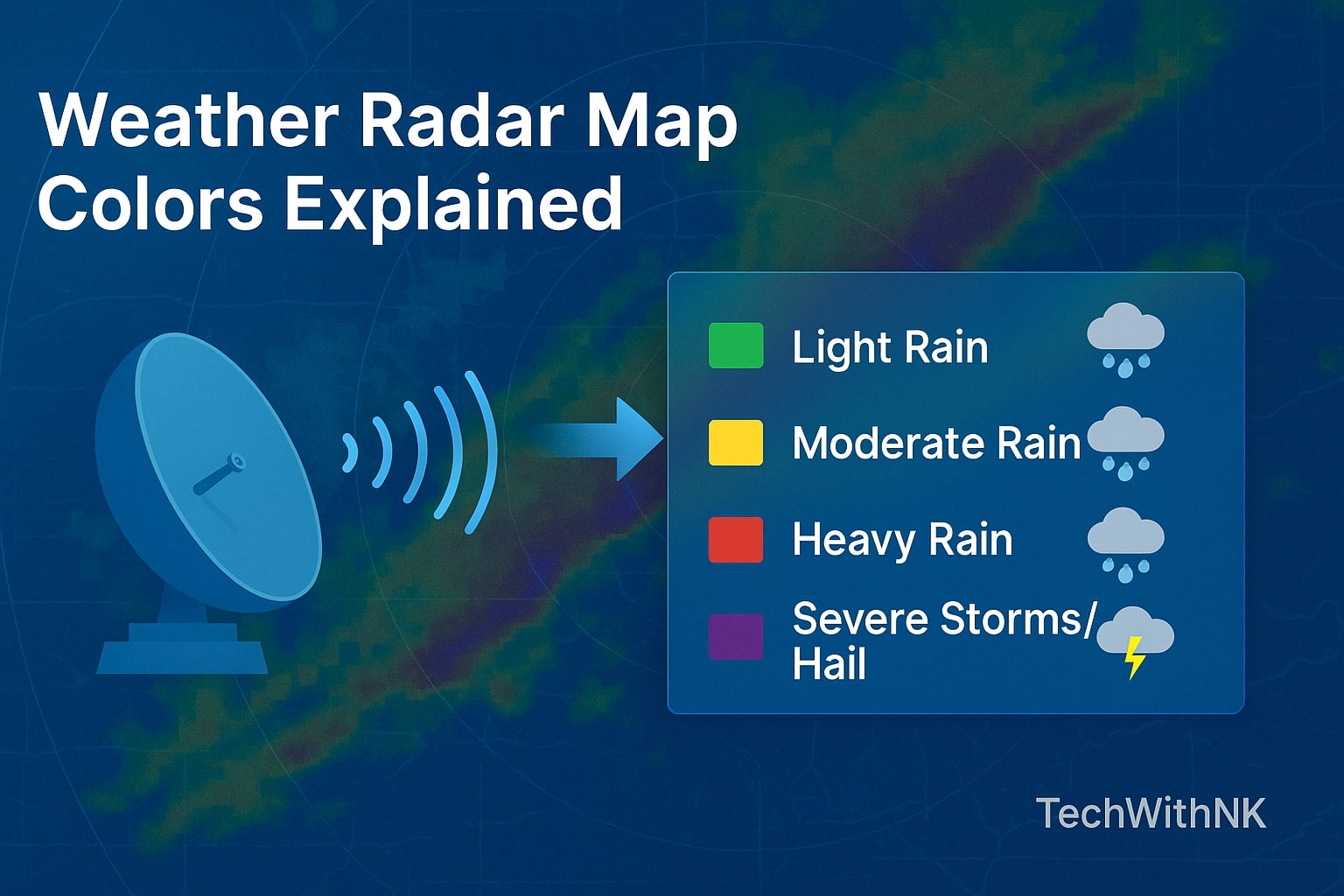
🗺️ Interpreting a Weather Radar Map
A weather radar map is one of the most widely used forecasting visuals today. Each color on the map represents precipitation intensity:
| Color | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Light Green | Light Rain |
| Dark Green | Moderate Rain |
| Yellow | Heavy Rain |
| Red | Very Heavy Rain / Storm |
| Purple | Extreme Hail or Tornado Activity |
By analyzing radar loops (animated radar images over time), forecasters can estimate storm movement, speed, and evolution—helping communities prepare for changing weather.
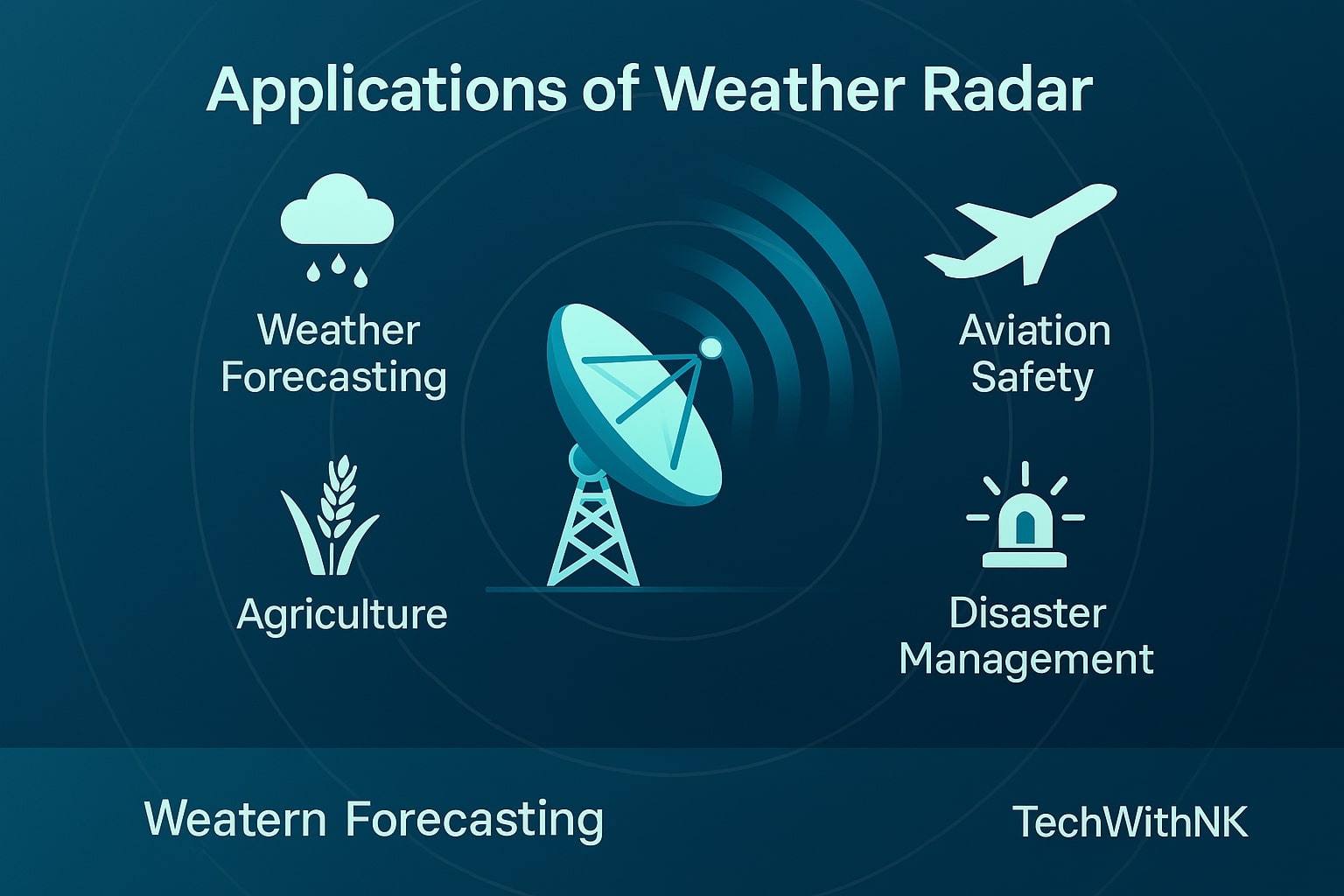
⚡ Weather Radar Applications in Forecasting and Safety
Weather radar applications extend far beyond simple rainfall detection. Some of the most critical uses include:
Severe Weather Warning Systems
Governments and meteorological agencies rely on live weather radar to detect developing thunderstorms, cyclones, and tornadoes.Aviation and Maritime Safety
Pilots use weather radar technology to avoid turbulent zones, while ships depend on radar data to navigate storms safely.Agriculture and Water Management
Farmers monitor weather radar maps to plan irrigation, harvesting, and crop protection.Disaster Preparedness and Emergency Response
Real-time Doppler weather radar data allows disaster agencies to coordinate evacuations and resource deployment ahead of storms.
🌦️ Global Weather Radar Networks
The world’s most advanced weather services—like the U.S. National Weather Service (NEXRAD), India Meteorological Department (IMD), and European EUMETNET—operate vast networks of radar stations.
India, for example, has installed Doppler radars across coastal and hilly regions to enhance cyclone and monsoon monitoring. These weather radar applications are vital for early warning and climate resilience, especially in densely populated or disaster-prone areas.
🌤️ Benefits of Weather Radar
Accurate short-term forecasts (nowcasting).
Enhanced disaster preparedness.
Real-time visibility into storm intensity.
Improved flight and shipping safety.
Support for research on climate patterns.
With constant upgrades, weather radar technology ensures we are never blind to what’s happening in the skies.
🧠 Future of Weather Radar
Next-generation radar systems are incorporating AI models, cloud-based analytics, and 5G data networks to enhance detection range and resolution. Soon, personal live weather radar apps could predict rain down to the minute and block level.
These developments promise a world where how weather radar works will be increasingly intelligent—fusing ground radar, satellite, and IoT weather sensors into one global forecasting network.
✅ Conclusion: Why Weather Radar Matters
In an age of climate uncertainty, weather radar is more than a forecasting tool—it’s a shield for humanity.
From tracking hurricanes to predicting local rainfall, weather radar applications empower us with the data needed to save lives, protect infrastructure, and plan daily activities.
Understanding how weather radar works helps us appreciate this silent guardian that scans the sky every second, ensuring communities around the world stay informed and safe.














