Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Have you ever wondered why India uses 230V 50Hz electricity, while countries like the USA use 120V 60Hz?
If you look at your charger, mixer grinder, refrigerator, or induction cooktop, you’ll always find 230V ~ 50Hz written on it.
But why exactly 230 volts?
Why 50 hertz?
Who decided this?
What is the science behind it?
In this simple, well-explained TechWithNK blog, you’ll learn:
The real reason behind India choosing 230V 50Hz
How voltage and frequency affect your home appliances
Historical reasons from British engineering
Technical advantages and disadvantages
Safety and efficiency impact
Why different countries use different systems
Will India ever switch to 60Hz?
Let’s understand everything step-by-step.
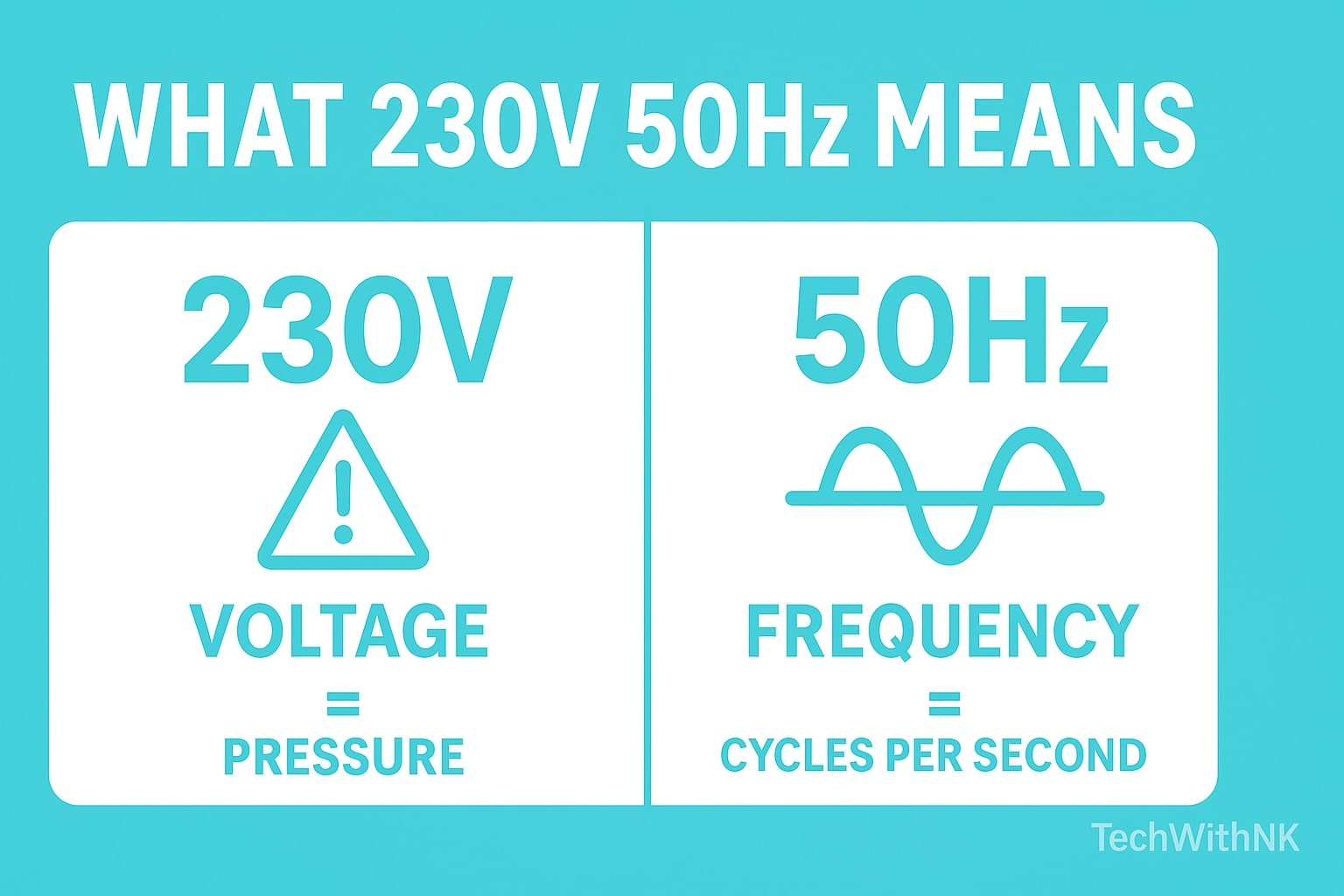
What Do 230V and 50Hz Mean? – Indian power supply explained
✔ 230V (Voltage)
Voltage is the pressure that pushes electric current through wires.
Higher voltage = more power can be delivered with less current
Lower voltage = more current is needed for the same power
Formula:
Power (W) = Voltage (V) × Current (A)
So, for the same 1000W appliance:
| Country | Voltage | Current Draw |
|---|---|---|
| India | 230V | ~4.3A |
| USA | 120V | ~8.3A |
This means India needs thinner and cheaper wires.
✔ 50Hz (Frequency)
Frequency is how many times the AC current changes direction in one second.
50Hz = 50 cycles per second
60Hz = 60 cycles per second
Higher frequency gives smoother operation for motors, but also increases losses in transmission.
Why Does India Use 230V 50Hz230V Electricity India ? (Real Reasons)
India did not choose this system randomly. There are five main reasons:
1.Historical Reason – British Influence
Why India Uses 230V 50Hz .Before independence, India’s electrical infrastructure was built mainly by British engineers.
The UK standard was:
240V
50Hz
Therefore India adopted the same standard for:
✔ power plants
✔ transformers
✔ motors
✔ home appliances
✔ wiring system
This historical choice became permanent because changing the entire grid later is almost impossible.
2.Technical Reason – Higher Voltage = Lower Current = Cheaper Infrastructure
why India uses 230V…India is a large country with millions of homes and long transmission lines.
Using 230V instead of 110V gives major benefits:
Less current flows for the same power
Wires can be thinner and cheaper
Transmission losses reduce
Transformers cost less
Overall national grid becomes more efficient
Example:
If India used 110V like the USA, we would need:
Thicker wires
Bigger transformers
More copper
Higher cost
This is not practical for a large developing nation.
3.Climate Factor – Higher Voltage Helps in Hot Regions
why India uses 230V…..India has a hot climate. In hot areas:
Wires heat up more
Current causes extra heating
Higher current = more heat
Using 230V reduces the current flow → reduces the heating effect.
4.Compatibility with European Standards
why India uses 230V…European nations (Germany, UK, France) use 220–240V, 50Hz.
India imports a lot of:
Motors
Household appliances
Electronic parts
Industrial machines
Using the same system ensures compatibility and lower cost.
5.Electrification Advantage – Covers More Area Efficiently
Higher voltage AC can travel longer distances with lower losses.
India’s vast rural electrification became easier with 230V 50Hz.
Why Do Some Countries Use 120V 60Hz Instead?
Countries like the USA, Canada, Japan use 120V 60Hz.
Reasons:
Earlier safety concerns with high voltage
Edison’s early DC systems influencing voltage levels
Local engineering standards
No British influence
Smaller country size (especially Japan)
But today, both systems are equally safe with proper wiring.
50Hz vs 60Hz – What’s Better?
Both have their pros and cons:
| Feature | 50Hz (India/Europe) | 60Hz (USA/Japan) |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Slightly lower | Slightly higher |
| Motor Speed | Slightly slower | Faster |
| Wire Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Losses | Higher | Lower |
| Appliance Life | Higher | Lower (sometimes) |
| Cost of Infrastructure | Cheaper | Expensive |
For large countries with high population density, 50Hz systems are cheaper and more practical.
Why 230V Instead of 220V or 240V?
arlier India used 240V.
To standardize globally, IEC introduced:
✔ 230V ± 10% (International standard)
So India updated the standard to match global compatibility.
Actual supply varies between 207V to 253V, depending on load.
Will India Ever Switch to 60Hz?
ery unlikely, because:
India’s entire electrical grid is already 50Hz
All industries rely on 50Hz motors
Changing frequency requires replacing every generator & transformer
Extremely expensive (hundreds of billions of dollars)
No real benefit
Therefore, India will continue using 230V 50Hz.
Conclusion- Why India Uses 230V 50Hz
dia uses the 230V 50Hz power supply mainly because of:
British historical influence
Lower current and cheaper infrastructure
Better efficiency for large transmission networks
Climate suitability
Standardization with Europe
This combination works perfectly for a large, hot, and rapidly growing country like India.
The 230V 50Hz system will continue for decades because switching now is nearly impossible.
Why India Uses 230V 50Hz – TechWithNK
Have you ever wondered why India uses 230V 50Hz electricity, while countries like the USA use 120V 60Hz?
If you look at your charger, mixer grinder, refrigerator, or induction cooktop, you’ll always find 230V ~ 50Hz written on it.
But why exactly 230 volts?
Why 50 hertz?
Who decided this?
What is the science behind it?
In this simple, well-explained TechWithNK blog, you’ll learn:














