Table of Contents
ToggleWireless Electricity Transfer – Is Tesla’s Dream Becoming Real?
Wireless electricity transfer – Is Tesla’s Dream Becoming Real? This question is becoming more relevant than ever as the world moves toward cable-free technology, smart ecosystems, and high-efficiency energy systems. The idea of sending power without wires feels futuristic, yet it was imagined more than 120 years ago by Nikola Tesla, one of the greatest inventors in history.
In recent years, rapid advancements in electromagnetic fields, resonant inductive coupling, and RF power transmission have brought us closer to achieving what once seemed impossible. From wireless chargers to room-scale power systems, engineers are reviving Tesla’s dream in new ways.
This blog explores how wireless power works, the modern wireless electricity transfer model, Tesla’s original vision, industries adopting this technology, and whether a wire-free future is truly possible.

⭐ 1. Nikola Tesla’s Vision – Far Ahead of His Time
Nikola Tesla first experimented with wireless power in the late 19th century. His famous Wardenclyffe Tower was designed to transmit electricity through the Earth’s natural resonance, allowing devices anywhere on the planet to receive energy without cables.
He imagined:
Wireless bulbs
Wireless motors
Wireless power for homes
A planet connected with energy like radio waves
Although the project remained incomplete due to financial and political issues, the core concept of tesla wireless electricity transfer inspired modern research.
Tesla once said:
“When wireless power is applied, the Earth will become a giant transformer.”
Today, his theories are evolving into real technologies.
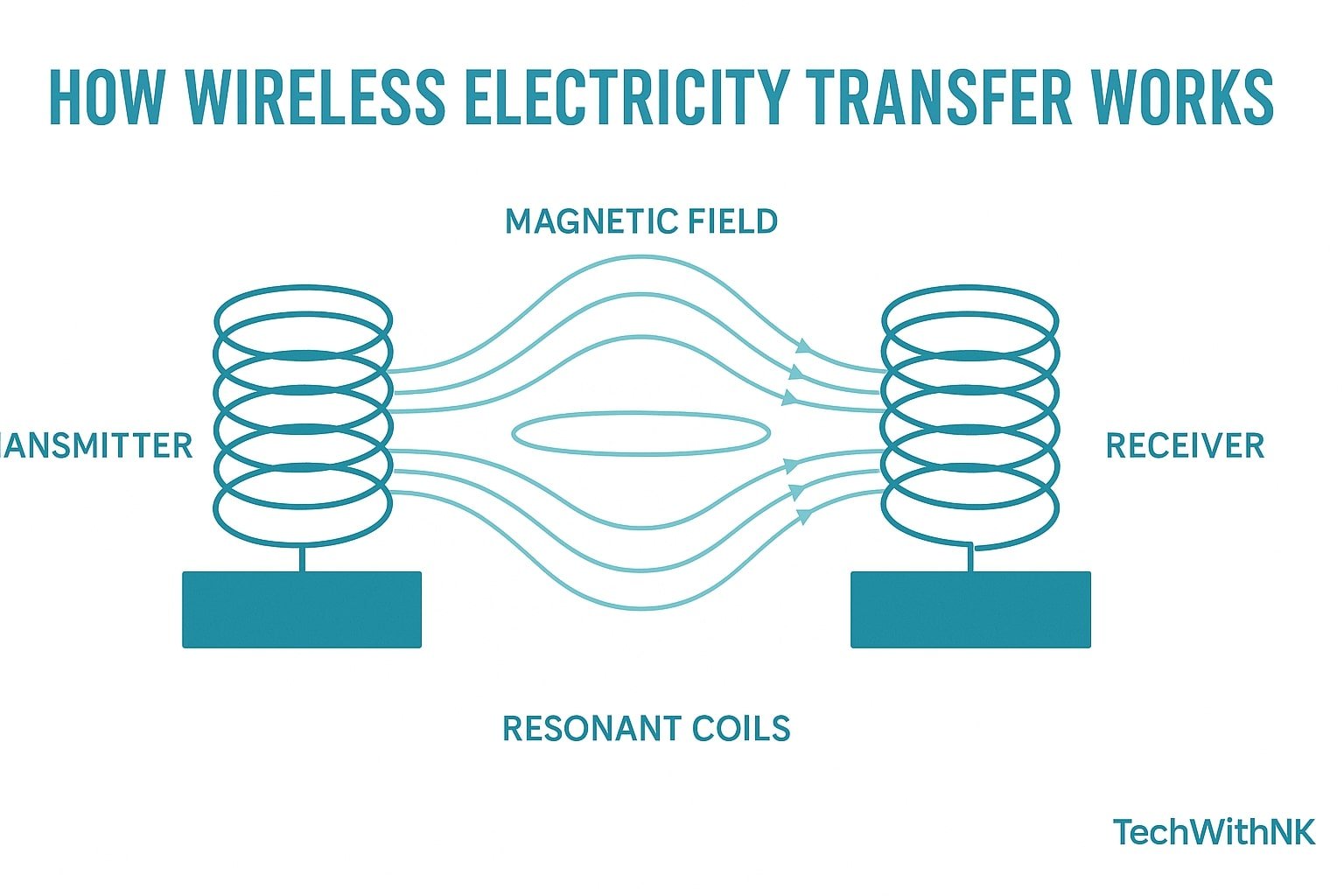
⭐ 2. How Modern Wireless Electricity Transfer Works
Modern systems do not use Tesla’s “Earth resonance” theory but rely on advanced physics. There are three major methods:
A. Inductive Coupling (Used in Qi Chargers)
Working Principle:
Two coils (transmitter and receiver) create a magnetic field. When placed close, energy transfers wirelessly.
Used in:
✔ Mobile wireless chargers
✔ Electric toothbrushes
✔ Smartwatches
Limitations:
❌ Very short range (a few millimeters)
❌ Low efficiency over distance
B. Resonant Inductive Coupling (Room-scale Power)
This is the core of most wireless electricity transfer models today.
How it works:
Two coils are tuned to the same frequency (resonance).
This increases range from a few millimeters to several meters.
Used in:
✔ Wireless charging pads
✔ Wireless kitchen appliances
✔ Room-based wireless power prototypes
C. Radio Frequency (RF) Power Transfer
Energy is transmitted using radio waves.
Advantages:
✔ Works at long distances
✔ Can charge low-power devices (sensors, IoT)
Limitations:
❌ Very low efficiency
❌ Cannot power high-watt appliances (yet)
D. Laser-Based Wireless Power
Laser beams send energy to a receiver (PV cell).
Used in:
✔ Drone charging
✔ Military projects
Limitation:
❌ Requires line of sight
❌ Safety concerns with high-power lasers
⭐ 3. Real-World Wireless Power Technologies (2025)
A modern wireless electricity transfer model includes:
1. Power Source
Electricity from grid/solar/battery
2. Transmitter Unit
A coil or RF antenna that generates electromagnetic waves
3. Medium
Air, magnetic field, or RF waves
4. Receiver Unit
Coil or rectenna (rectifying antenna) inside the device
5. Load
The device that consumes power (phone, drone, home appliance)
Efficiency depends on:
Distance
Alignment
Frequency
Coil design
Obstructions
Engineers try to balance efficiency with safety and usability.
⭐ 4. The Wireless Electricity Transfer Model – Explained
The device that consumes power (phone, drone, home appliance)
Efficiency depends on:
Distance
Alignment
Frequency
Coil design
Obstructions
Engineers try to balance efficiency with safety and usability.
⭐ 5. Is Tesla’s Dream Becoming Real?
The short answer: Partially, but not fully yet.
What Has Become Real
✔ Wireless charging exists
✔ Room-scale wireless power prototypes work
✔ EV wireless charging is commercial
✔ RF charging for IoT is widespread
✔ Medical implants work wirelessly
✔ Drones can charge in mid-air
What Is Still a Dream
❌ Sending massive power wirelessly across cities
❌ Worldwide wireless grid
❌ Zero-loss wireless transmission
❌ High-watt appliances without cables
Tesla imagined a world where power was as freely accessible as radio waves.
Today, we have achieved localized wireless power—not planet-scale power.
⭐ 6. Advantages of Wireless Electricity Transfer
1. No More Cables
Reduces clutter, improves aesthetics, and boosts convenience.
2. Safer in Hazardous Areas
No sparks, no exposed wires—ideal for:
Chemical plants
Hospitals
Outdoor environments
3. Durable & Weatherproof
Devices without charging ports are more reliable.
4. Mobility
EVs, drones, and robots can charge while moving using hotspots.
5. Supports IoT & Smart Homes
Small sensors can run for years without batteries.
⭐ 7. Limitations of Wireless Electricity Transfer
1. Lower Efficiency
Wired charging = 95% efficient
Wireless charging = ~50–70%
2. Limited Range
Most systems work within a few centimeters to meters.
3. High Cost
Advanced coils and transmitters are expensive.
4. Safety Concerns
High-power RF or lasers require strict safety rules.
5. Infrastructure Changes
Homes, offices, roads must install transmitter networks.
⭐ 8. Safety of Wireless Electricity Transfer
Researchers follow strict regulations:
FCC rules for RF exposure
ICNIRP radiation guidelines
Thermal safety limits
Beam shaping technology for lasers
Foreign-object-detection to avoid heating metal
Most consumer wireless chargers are completely safe.
⭐ 9. Future of Wireless Electricity (2025–2040)
1. Wireless Smart Homes
Rooms where devices automatically charge anywhere.
2. Wireless Road Charging for EVs
EVs charging while driving on highways.
3. Space-Based Solar Power
Satellites collecting solar energy and sending it to Earth wirelessly.
4. Wireless Power Grids
Local regions powered by resonant towers.
5. Long-Range Laser Power Transmission
For drones, military bases, and remote industries.
⭐ 10. Final Answer: Is Tesla’s Dream Becoming Real?
Yes—partially.
Wireless electricity transfer – Is Tesla’s Dream Becoming Real?
We have achieved wireless charging on small scales, and the technology is expanding fast. But Tesla’s grand vision of global wireless energy is still far from reality.
However, if progress continues at current speed, the next 10–20 years may witness revolutionary breakthroughs.
Tesla was right.
Wireless power is the future—just arriving later than he imagined.